Page 105 - Read Online
P. 105
Page 10 of 16 Cadamuro et al. Hepatoma Res 2022;8:11 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2021.140
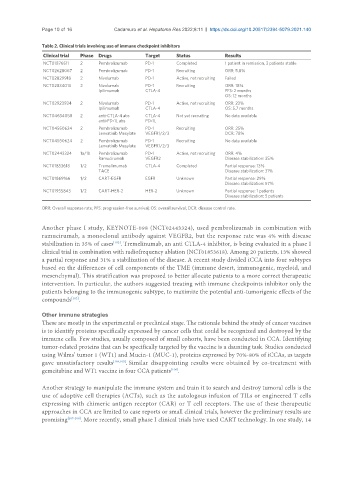
Table 2. Clinical trials involving use of immune checkpoint inhibitors
Clinical trial Phase Drugs Target Status Results
NCT01876511 2 Pembrolizumab PD-1 Completed 1 patient in remission, 3 patients stable
NCT02628067 2 Pembrolizumab PD-1 Recruiting ORR: 5.8%
NCT02829918 2 Nivolumab PD-1 Active, not recruiting Failed
NCT02834013 2 Nivolumab PD-1 Recruiting ORR: 18%
Ipilimumab CTLA-4 PFS: 2 months
OS: 12 months
NCT02923934 2 Nivolumab PD-1 Active, not recruiting ORR: 23%
Ipilimumab CTLA-4 OS: 5.7 months
NCT04634058 2 anti-CTLA-4 abs CTLA-4 Not yet recruiting No data available
anti-PD-1L abs PD-1L
NCT04550624 2 Pembrolizumab PD-1 Recruiting ORR: 25%
Lenvatinib Mesylate VEGFR1/2/3 DCR: 78%
NCT04550624 2 Pembrolizumab PD-1 Recruiting No data available
Lenvatinib Mesylate VEGFR1/2/3
NCT02443324 1a/1b Pembrolizumab PD-1 Active, not recruiting ORR: 4%
Ramucirumab VEGFR2 Disease stabilization: 35%
NCT01853618 1/2 Tremelimumab CTLA-4 Completed Partial response: 13%
TACE Disease stabilization: 31%
NCT01869166 1/2 CART-EGFR EGFR Unknown Partial response: 29%
Disease stabilization: 57%
NCT01935843 1/2 CART-HER-2 HER-2 Unknown Partial response: 1 patients
Disease stabilization: 5 patients
ORR: Overall response rate; PFS: progression-free survival; OS: overall survival; DCR: disease control rate.
Another phase I study, KEYNOTE-098 (NCT02443324), used pembrolizumab in combination with
ramucirumab, a monoclonal antibody against VEGFR2, but the response rate was 4% with disease
stabilization in 35% of cases . Tremelinumab, an anti CTLA-4 inhibitor, is being evaluated in a phase I
[102]
clinical trial in combination with radiofrequency ablation (NCT01853618). Among 20 patients, 13% showed
a partial response and 31% a stabilization of the disease. A recent study divided iCCA into four subtypes
based on the differences of cell components of the TME (immune desert, immunogenic, myeloid, and
mesenchymal). This stratification was proposed to better allocate patients to a more correct therapeutic
intervention. In particular, the authors suggested treating with immune checkpoints inhibitor only the
patients belonging to the immunogenic subtype, to maximize the potential anti-tumorigenic effects of the
[103]
compounds .
Other immune strategies
These are mostly in the experimental or preclinical stage. The rationale behind the study of cancer vaccines
is to identify proteins specifically expressed by cancer cells that could be recognized and destroyed by the
immune cells. Few studies, usually composed of small cohorts, have been conducted in CCA. Identifying
tumor-related proteins that can be specifically targeted by the vaccine is a daunting task. Studies conducted
using Wilms’ tumor 1 (WT1) and Mucin-1 (MUC-1), proteins expressed by 70%-80% of iCCAs, as targets
gave unsatisfactory results [104,105] . Similar disappointing results were obtained by co-treatment with
gemcitabine and WT1 vaccine in four CCA patients .
[106]
Another strategy to manipulate the immune system and train it to search and destroy tumoral cells is the
use of adoptive cell therapies (ACTs), such as the autologous infusion of TILs or engineered T cells
expressing with chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) or T cell receptors. The use of these therapeutic
approaches in CCA are limited to case reports or small clinical trials, however the preliminary results are
promising [107-109] . More recently, small phase I clinical trials have used CART technology. In one study, 14