Page 17 - Read Online
P. 17
Page 8 of 12 Hiyama et al. Hepatoma Res 2021;7:44 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2021.21
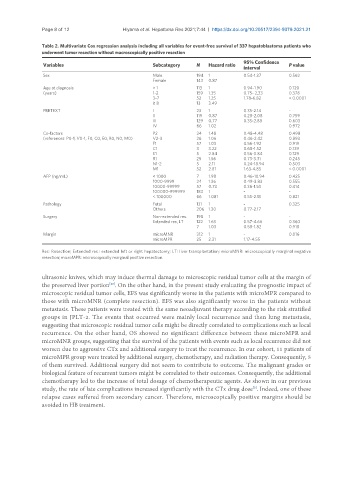
Table 2. Multivariate Cox regression analysis including all variables for event-free survival of 337 hepatoblastoma patients who
underwent tumor resection without macroscopically positive resection
95% Confidence
Variables Subcategory N Hazard ratio P value
interval
Sex Male 194 1 0.54-1.37 0.562
Female 143 0.87
Age at diagnosis > 1 113 1 0.94-1.90 0.120
(years) 1-2 159 1.35 0.75- 2,33 0.378
3-7 52 1.25 1.78-6.82 < 0.0001
≥ 8 13 3.49
PRETEXT I 23 1 0.35-2.14 -
II 119 0.87 0.28-2.08 0.759
III 129 0.77 0.35-2.88 0.603
IV 66 1.02 0.972
Co-factors P2 24 1.48 0.48-4.48 0.498
(references: P0-1, V0-1, F0, C0, E0, R0, N0, M0) V2-3 26 1.06 0.46-2.42 0.893
F1 57 1.03 0.56-1.92 0.919
C1 3 3.22 0.68-1.52 0.139
E1 5 2.84 0.56-3.84 0.129
R1 25 1.56 0.73-3.31 0.245
N1-2 5 2.11 0.24-18.94 0.503
M1 52 2.81 1.63-4.85 < 0.0001
AFP (ng/mL) < 1000 7 1.98 0.46-10.94 0.425
1000-9999 24 1.36 0.49-3.83 0.555
10000-99999 57 0.73 0.36-1.53 0.414
100000-999999 183 1 - -
< 100000 66 1.081 0.55-2.13 0.821
Pathology Fetal 131 1 - 0.325
Others 206 1.30 0.77-2.17
Surgery Non-extended res. 198 1 - -
Extended res, LT 122 1.63 0.57-4.66 0.360
7 1.03 0.58-1.82 0.918
Margin microMNR 312 1 - 0.016
microMPR 25 2.31 1.17-4.55
Res: Resection; Extended res.: extended left or right hepatectomy; LT: liver transplantation; microMNR: microscopically marginal negative
resection; microMPR: microscopically marginal positive resection.
ultrasonic knives, which may induce thermal damage to microscopic residual tumor cells at the margin of
the preserved liver portion . On the other hand, in the present study evaluating the prognostic impact of
[28]
microscopic residual tumor cells, EFS was significantly worse in the patients with microMPR compared to
those with microMNR (complete resection). EFS was also significantly worse in the patients without
metastasis. These patients were treated with the same neoadjuvant therapy according to the risk stratified
groups in JPLT-2. The events that occurred were mainly local recurrence and then lung metastasis,
suggesting that microscopic residual tumor cells might be directly correlated to complications such as local
recurrence. On the other hand, OS showed no significant difference between these microMPR and
microMNR groups, suggesting that the survival of the patients with events such as local recurrence did not
worsen due to aggressive CTx and additional surgery to treat the recurrence. In our cohort, 11 patients of
microMPR group were treated by additional surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. Consequently, 5
of them survived. Additional surgery did not seem to contribute to outcome. The malignant grades or
biological feature of recurrent tumors might be correlated to their outcomes. Consequently, the additional
chemotherapy led to the increase of total dosage of chemotherapeutic agents. As shown in our previous
study, the rate of late complications increased significantly with the CTx drug dose . Indeed, one of these
[3]
relapse cases suffered from secondary cancer. Therefore, microscopically positive margins should be
avoided in HB treatment.