Page 54 - Read Online
P. 54
Armstrong et al. Hepatoma Res 2021;7:18 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2020.118 Page 7 of 12
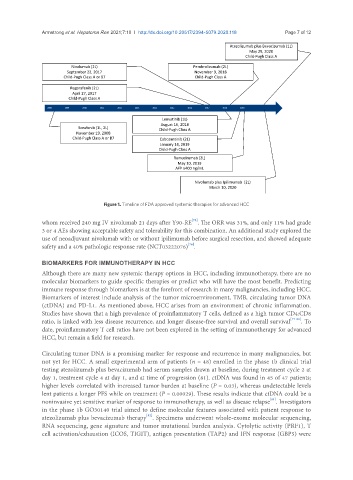
Atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab (1L)
May 29, 2020
Child-Pugh Class A
Nivolumab (2L) Pembrolizumab (2L)
September 22, 2017 November 9, 2018
Child-Pugh Class A or B7 Child-Pugh Class A
Regorafenib (2L)
April 27, 2017
Child-Pugh Class A
2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019
Lenvatinib (1L)
August 16, 2018
Sorafenib (1L, 2L) Child-Pugh Class A
November 19, 2008
Child-Pugh Class A or B7 Cabozantinib (2L)
January 14, 2019
Child-Pugh Class A
Ramucirumab (2L)
May 10, 2019
AFP ≥400 ng/mL
Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab (2L)
March 10, 2020
Figure 1. Timeline of FDA approved systemic therapies for advanced HCC
[75]
whom received 240 mg IV nivolumab 21 days after Y90-RE . The ORR was 31%, and only 11% had grade
3 or 4 AEs showing acceptable safety and tolerability for this combination. An additional study explored the
use of neoadjuvant nivolumab with or without ipilimumab before surgical resection, and showed adequate
safety and a 40% pathologic response rate (NCT03222076) .
[76]
BIOMARKERS FOR IMMUNOTHERAPY IN HCC
Although there are many new systemic therapy options in HCC, including immunotherapy, there are no
molecular biomarkers to guide specific therapies or predict who will have the most benefit. Predicting
immune response through biomarkers is at the forefront of research in many malignancies, including HCC.
Biomarkers of interest include analysis of the tumor microenvironment, TMB, circulating tumor DNA
(ctDNA) and PD-L1. As mentioned above, HCC arises from an environment of chronic inflammation.
Studies have shown that a high prevalence of proinflammatory T cells, defined as a high tumor CD4:CD8
ratio, is linked with less disease recurrence, and longer disease-free survival and overall survival [77-80] . To
date, proinflammatory T cell ratios have not been explored in the setting of immunotherapy for advanced
HCC, but remain a field for research.
Circulating tumor DNA is a promising marker for response and recurrence in many malignancies, but
not yet for HCC. A small experimental arm of patients (n = 48) enrolled in the phase 1b clinical trial
testing atezolizumab plus bevacizumab had serum samples drawn at baseline, during treatment cycle 2 at
day 1, treatment cycle 4 at day 1, and at time of progression (81). ctDNA was found in 45 of 47 patients;
higher levels correlated with increased tumor burden at baseline (P = 0.03), whereas undetectable levels
lent patients a longer PFS while on treatment (P = 0.00029). These results indicate that ctDNA could be a
[81]
noninvasive yet sensitive marker of response to immunotherapy, as well as disease relapse . Investigators
in the phase 1b GO30140 trial aimed to define molecular features associated with patient response to
[82]
atezolizumab plus bevacizumab therapy . Specimens underwent whole-exome molecular sequencing,
RNA sequencing, gene signature and tumor mutational burden analysis. Cytolytic activity (PRF1), T
cell activation/exhaustion (ICOS, TIGIT), antigen presentation (TAP2) and IFN response (GBP5) were