Page 107 - Read Online
P. 107
Page 10 of 16 Brunsing et al. Hepatoma Res 2020;6:59 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2020.50
A
B
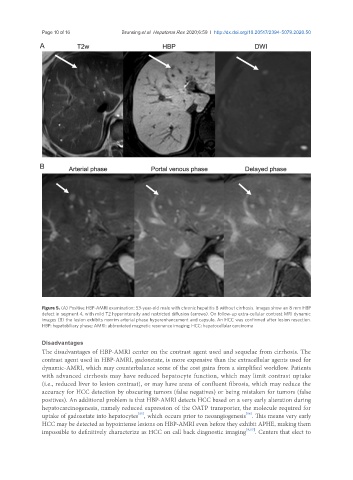
Figure 5. (A) Positive HBP-AMRI examination: 53-year-old male with chronic hepatitis B without cirrhosis. Images show an 8 mm HBP
defect in segment 4, with mild T2 hyperintensity and restricted diffusion (arrows). On follow-up extra-cellular contrast MRI dynamic
images (B) the lesion exhibits nonrim arterial phase hyperenhancement and capsule. An HCC was confirmed after lesion resection.
HBP: hepatobiliary phase; AMRI: abbreviated magnetic resonance imaging; HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of HBP-AMRI center on the contrast agent used and sequelae from cirrhosis. The
contrast agent used in HBP-AMRI, gadoxetate, is more expensive than the extracellular agents used for
dynamic-AMRI, which may counterbalance some of the cost gains from a simplified workflow. Patients
with advanced cirrhosis may have reduced hepatocyte function, which may limit contrast uptake
(i.e., reduced liver to lesion contrast), or may have areas of confluent fibrosis, which may reduce the
accuracy for HCC detection by obscuring tumors (false negatives) or being mistaken for tumors (false
positives). An additional problem is that HBP-AMRI detects HCC based on a very early alteration during
hepatocarcinogenesis, namely reduced expression of the OATP transporter, the molecule required for
[56]
[55]
uptake of gadoxetate into hepatocytes , which occurs prior to neoangiogenesis . This means very early
HCC may be detected as hypointense lesions on HBP-AMRI even before they exhibit APHE, making them
impossible to definitively characterize as HCC on call back diagnostic imaging [9,57] . Centers that elect to