Page 40 - Read Online
P. 40
Dai et al. Hepatoma Res 2020;6:16 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2019.40 Page 3 of 9
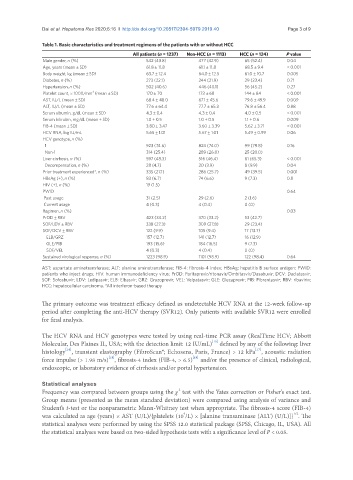
Table 1. Basic characteristics and treatment regimens of the patients with or without HCC
All patients (n = 1237) Non-HCC (n = 1113) HCC (n = 124) P value
Male gender, n (%) 542 (43.8) 477 (42.9) 65 (52.4) 0.04
Age, years (mean ± SD) 61.8 ± 11.8 61.1 ± 11.8 68.5 ± 9.4 < 0.001
Body weight, kg (mean ± SD) 63.7 ± 12.4 64.0 ± 12.5 61.0 ± 10.7 0.005
Diabetes, n (%) 273 (22.1) 244 (21.9) 29 (23.4) 0.71
Hypertension, n (%) 502 (40.6) 446 (40.1) 56 (45.2) 0.27
3
Platelet count, × 1000/mm (mean ± SD) 170 ± 70 173 ± 68 144 ± 84 < 0.001
AST, IU/L (mean ± SD) 68.4 ± 48.0 67.1 ± 45.6 79.6 ± 49.9 0.009
ALT, IU/L (mean ± SD) 77.6 ± 64.4 77.7 ± 65.3 76.8 ± 56.4 0.88
Serum albumin, g/dL (mean ± SD) 4.3 ± 0.4 4.3 ± 0.4 4.0 ± 0.5 < 0.001
Serum bilirubin, mg/dL (mean ± SD) 1.0 ± 0.5 1.0 ± 0.5 1.1 ± 0.6 0.009
FIB-4 (mean ± SD) 3.80 ± 3.47 3.60 ± 3.39 5.62 ± 3.71 < 0.001
HCV RNA, log IU/mL 5.65 ± 1.01 5.67 ± 1.01 5.49 ± 0.99 0.06
HCV genotype, n (%)
1 923 (74.6) 824 (74.0) 99 (79.8) 0.16
Non-1 314 (25.4) 289 (26.0) 25 (20.0)
Liver cirrhosis, n (%) 597 (48.3) 516 (46.4) 81 (65.3) < 0.001
Decompensation, n (%) 28 (4.7) 20 (3.9) 8 (9.9) 0.04
Prior treatment experienced*, n (%) 335 (27.1) 286 (25.7) 49 (39.5) 0.001
HBsAg (+), n (%) 83 (6.7) 74 (6.6) 9 (7.3) 0.8
HIV (+), n (%) 19 (1.5)
PWID 0.64
Past usage 31 (2.5) 29 (2.6) 2 (1.6)
Current usage 4 (0.3) 4 (0.4) 0 (0)
Regimen, n (%) 0.03
PrOD ± RBV 423 (34.2) 370 (33.2) 53 (42.7)
SOF/LDV ± RBV 338 (27.3) 309 (27.8) 29 (23.4)
SOF/DCV ± RBV 122 (9.9) 105 (9.4) 17 (13.7)
ELB/GRZ 157 (12.7) 141 (12.7) 16 (12.9)
GLE/PIB 193 (15.6) 184 (16.5) 9 (7.3)
SOF/VEL 4 (0.3) 4 (0.4) 0 (0)
Sustained virological response, n (%) 1223 (98.9) 1101 (98.9) 122 (98.4) 0.64
AST: aspartate aminotransferase; ALT: alanine aminotransferase; FIB-4: fibrosis-4 index; HBsAg: hepatitis B surface antigen; PWID:
patients who inject drugs; HIV: human immunodeficiency virus; PrOD: Paritaprevir/ritonavir/Ombitasvir/Dasabuvir; DCV: Daclatasvir;
SOF: Sofosbuvir; LDV: Ledipasvir; ELB: Elbasvir; GRZ: Grazoprevir; VEL: Velpatasvir; GLE: Glecaprevir; PIB: Pibrentasvir; RBV: ribavirin;
HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma. *All interferon-based therapy
The primary outcome was treatment efficacy defined as undetectable HCV RNA at the 12-week follow-up
period after completing the anti-HCV therapy (SVR12). Only patients with available SVR12 were enrolled
for final analysis.
The HCV RNA and HCV genotypes were tested by using real-time PCR assay (RealTime HCV; Abbott
[15]
Molecular, Des Plaines IL, USA; with the detection limit: 12 IU/mL) defined by any of the following: liver
[17]
[16]
histology , transient elastography (FibroScan®; Echosens, Paris, France) > 12 kPa , acoustic radiation
[19]
[18]
force impulse (> 1.98 m/s) , fibrosis-4 index (FIB-4, > 6.5) and/or the presence of clinical, radiological,
endoscopic, or laboratory evidence of cirrhosis and/or portal hypertension.
Statistical analyses
2
Frequency was compared between groups using the χ test with the Yates correction or Fisher’s exact test.
Group means (presented as the mean standard deviation) were compared using analysis of variance and
Student’s t-test or the nonparametric Mann-Whitney test when appropriate. The fibrosis-4 score (FIB-4)
1/2
was calculated as age (years) × AST (U/L)/{platelets (10 /L) × [alanine transaminase (ALT) (U/L)]} . The
9
statistical analyses were performed by using the SPSS 12.0 statistical package (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA). All
the statistical analyses were based on two-sided hypothesis tests with a significance level of P < 0.05.