Page 71 - Read Online
P. 71
Page 6 of 16 Chávez-López et al. Hepatoma Res 2020;6:14 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2019.023
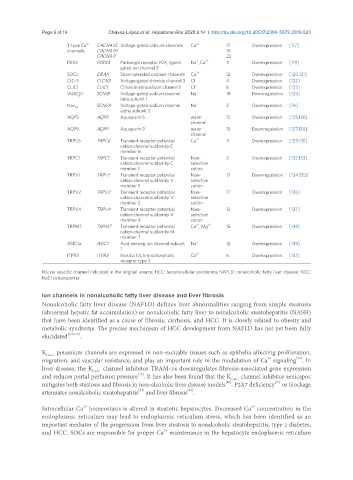
2+
T-type Ca CACNA1G Voltage-gated calcium channels Ca 2+ 17 Overexpression [117]
channels CACNA1H 16
CACNA1I 22
+
P2X3 P2RX3 Purinergic receptor P2X, ligand Na , Ca 2+ 11 Overexpression [119]
gated ion channel 3
SOCs ORAI1 Store-operated calcium channels Ca 2+ 12 Overexpression [120,121]
CIC-3 CLCN3 Voltage-gated chloride channel 3 Cl - 4 Overexpression [122]
CLIC1 CLIC1 Chloride intracellular channel 1 Cl - 6 Overexpression [123]
VGSCβ1 SCN1B Voltage-gated sodium channel Na + 19 Downregulation [124]
beta subunit 1
SCN2A Voltage-gated sodium channel Na + 2 Overexpression [96]
Nav 1.2
alpha subunit 2
AQP5 AQP5 Aquaporin 5 water 12 Overexpression [125,126]
channel
AQP9 AQP9 Aquaporin 9 water 15 Downregulation [127,128]
channel
TRPC6 TRPC6 Transient receptor potential Ca 2+ 11 Overexpression [129-131]
cation channel subfamily C
member 6
TRPC1 TRPC1 Transient receptor potential Non- 3 Overexpression [132,133]
cation channel subfamily C selective
member 1 cation
TRPV1 TRPV1 Transient receptor potential Non- 17 Downregulation [134,135]
cation channel subfamily V selective
member 1 cation
TRPV2 TRPV2 Transient receptor potential Non- 17 Overexpression [136]
cation channel subfamily V selective
member 2 cation
TRPV4 TRPV4 Transient receptor potential Non- 12 Overexpression [137]
cation channel subfamily V selective
member 4 cation
2+
TRPM7 TRPM7 Transient receptor potential Ca , Mg 2+ 15 Overexpression [138]
cation channel subfamily M
member 7
ASIC1a ASIC1 Acid sensing ion channel subunit Na + 12 Overexpression [139]
1
ITPR3 ITPR3 Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate Ca 2+ 6 Overexpression [141]
receptor type 3
NS: no specific channel indicated in the original source; HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; NAFLD: nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; NCC:
NaCl cotransporter
Ion channels in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and liver fibrosis
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) defines liver abnormalities ranging from simple steatosis
(abnormal hepatic fat accumulation) or nonalcoholic fatty liver to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)
that have been identified as a cause of fibrosis, cirrhosis, and HCC. It is closely related to obesity and
metabolic syndrome. The precise mechanism of HCC development from NAFLD has not yet been fully
elucidated [3,75-77] .
K Ca3.1 potassium channels are expressed in non-excitable tissues such as epithelia affecting proliferation,
[78]
2+
migration, and vascular resistance, and play an important role in the modulation of Ca signaling . In
liver disease, the K Ca3.1 channel inhibitor TRAM-34 downregulates fibrosis-associated gene expression
[79]
and reduces portal perfusion pressure . It has also been found that the K Ca3.1 channel inhibitor senicapoc
[80]
[81]
mitigates both steatosis and fibrosis in non-alcoholic liver disease models . P2X7 deficiency or blockage
[83]
[82]
attenuates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis .
2+
2+
Intracellular Ca homeostasis is altered in steatotic hepatocytes. Decreased Ca concentration in the
endoplasmic reticulum may lead to endoplasmic reticulum stress, which has been identified as an
important mediator of the progression from liver steatosis to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, type 2 diabetes,
and HCC. SOCs are responsible for proper Ca maintenance in the hepatocyte endoplasmic reticulum
2+