Page 32 - Read Online
P. 32
Guerriero et al. Hepatoma Res 2019;5:6 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2018.108 Page 3 of 22
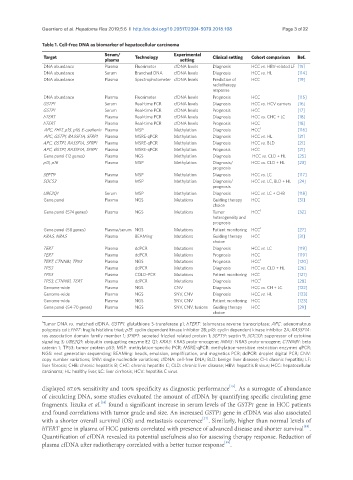
Table 1. Cell-free DNA as biomarker of hepatocellular carcinoma
Target Serum/ Technology Experimental Clinical setting Cohort comparison Ref.
plasma setting
DNA abundance Plasma Fluorimeter cfDNA levels Diagnosis HCC vs. HBV-related LF [15]
DNA abundance Serum Branched DNA cfDNA levels Diagnosis HCC vs. HL [114]
DNA abundance Plasma Spectrophotometer cfDNA levels Prediction of HCC [19]
radiotherapy
response
DNA abundance Plasma Fluorimeter cfDNA levels Prognosis HCC [115]
GSTP1 Serum Real-time PCR cfDNA levels Diagnosis HCC vs. HCV carriers [16]
GSTP1 Serum Real-time PCR cfDNA levels Prognosis HCC [17]
hTERT Plasma Real-time PCR cfDNA levels Diagnosis HCC vs. CHC + LC [18]
hTERT Plasma Real-time PCR cfDNA levels Prognosis HCC [18]
APC, FHIT, p15, p16, E-cadherin Plasma MSP Methylation Diagnosis HCC 1 [116]
APC, GSTP1, RASSF1A, SFRP1 Plasma MSRE-qPCR Methylation Diagnosis HCC vs. HL [21]
APC, GSTP1, RASSF1A, SFRP1 Plasma MSRE-qPCR Methylation Diagnosis HCC vs. BLD [21]
APC, GSTP1, RASSF1A, SFRP1 Plasma MSRE-qPCR Methylation Prognosis HCC [21]
Gene panel (12 genes) Plasma NGS Methylation Diagnosis HCC vs. CLD + HL [25]
p15, p16 Plasma MSP Methylation Diagnosis/ HCC vs. CLD + HL [23]
prognosis
SEPT9 Plasma MSP Methylation Diagnosis HCC vs. LC [117]
SOCS3 Plasma MSP Methylation Diagnosis/ HCC vs. LC, BLD + HL [24]
prognosis
UBE2Q1 Serum MSP Methylation Diagnosis HCC vs. LC + CHB [118]
Gene panel Plasma NGS Mutations Guiding therapy HCC [31]
choice
Gene panel (574 genes) Plasma NGS Mutations Tumor HCC 1 [32]
heterogeneity and
prognosis
Gene panel (58 genes) Plasma/serum NGS Mutations Patient monitoring HCC 1 [27]
KRAS, NRAS Plasma BEAMing Mutations Guiding therapy HCC [31]
choice
TERT Plasma ddPCR Mutations Diagnosis HCC vs. LC [119]
TERT Plasma ddPCR Mutations Prognosis HCC [119]
TERT, CTNNB1, TP53 Plasma NGS Mutations Prognosis HCC 1 [120]
TP53 Plasma ddPCR Mutations Diagnosis HCC vs. CLD + HL [26]
TP53 Plasma COLD-PCR Mutations Patient monitoring HCC [121]
TP53, CTNNB1, TERT Plasma ddPCR Mutations Diagnosis HCC 1 [28]
Genome-wide Plasma NGS CNV Diagnosis HCC vs. CH + LC [122]
Genome-wide Plasma NGS SNV, CNV Diagnosis HCC vs. HL [123]
Genome-wide Plasma NGS SNV, CNV Patient monitoring HCC [123]
Gene panel (54-70 genes) Plasma NGS SNV, CNV, fusions Guiding therapy HCC [29]
choice
1 Tumor DNA vs. matched cfDNA. GSTP1: glutathione S-transferase p1; hTERT: telomerase reverse transcriptase; APC: adenomatous
polyposis coli; FHIT: fragile histidine triad; p15: cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 2B; p16: cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 2A; RASSF1A:
ras association domain family member 1; SFRP1: secreted frizzled related protein 1; SEPT9: septin 9; SOCS3 : suppressor of cytokine
signaling 3; UBE2Q1: ubiquitin conjugating enzyme E2 Q1; KRAS: KRAS proto-oncogene; NRAS: NRAS proto-oncogene; CTNNB1: beta
catenin 1; TP53: tumor protein p53; MSP: methylation-specific PCR; MSRE-qPCR: methylation-sensitive restriction enzymes qPCR;
NGS: next generation sequencing; BEAMing: beads, emulsion, amplification, and magnetics PCR; ddPCR: droplet digital PCR; CNV:
copy number variations; SNV: single nucleotide variations; cfDNA: cell-free DNA; BLD: benign liver disease; CH: chronic hepatitis; LF:
liver fibrosis; CHB: chronic hepatitis B; CHC: chronic hepatitis C; CLD: chronic liver disease; HBV: hepatitis B virus; HCC: hepatocellular
carcinoma; HL: healthy liver; LC: liver cirrhosis; HCV: hepatitis C virus
displayed 87.0% sensitivity and 100% specificity as diagnostic performance . As a surrogate of abundance
[15]
of circulating DNA, some studies evaluated the amount of cfDNA by quantifying specific circulating gene
fragments. Iizuka et al. found a significant increase in serum levels of the GSTP1 gene in HCC patients
[16]
and found correlations with tumor grade and size. An increased GSTP1 gene in cfDNA was also associated
[17]
with a shorter overall survival (OS) and metastasis occurrence . Similarly, higher than normal levels of
[18]
hTERT gene in plasma of HCC patients correlated with presence of advanced disease and shorter survival .
Quantification of cfDNA revealed its potential usefulness also for assessing therapy response. Reduction of
[19]
plasma cfDNA after radiotherapy correlated with a better tumor response .