Page 169 - Read Online
P. 169
Page 6 of 11 Tamai. Hepatoma Res 2018;4:75 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2018.98
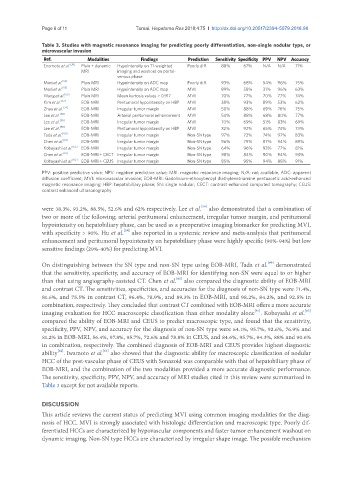
Table 3. Studies with magnetic resonance imaging for predicting poorly differentiation, non-single nodular type, or
microvascular invasion
Ref. Modalities Findings Prediction Sensitivity Specificity PPV NPV Accuracy
Enomoto et al. [38] Plain + dynamic Hypointensity on T1-weighted Poorly diff. 88% 67% N/A N/A 71%
MRI imaging and washout on portal-
venous phase
Mori et al. [53] Plain MRI Hypointensity on ADC map Poorly diff. 93% 68% 54% 96% 75%
Mori et al. [53] Plain MRI Hypointensity on ADC map MVI 89% 58% 31% 96% 63%
Wang et al. [55] Plain MRI Mean kurtosis values > 0.917 MVI 70% 77% 70% 77% 74%
Kim et al. [57] EOB-MRI Peritumoral hypointensity on HBP MVI 38% 93% 89% 53% 62%
Zhao et al. [54] EOB-MRI Irregular tumor margin MVI 50% 88% 69% 76% 75%
Lee et al. [58] EOB-MRI Arterial peritumoral enhancement MVI 54% 88% 68% 80% 77%
Lee et al. [58] EOB-MRI Irregular tumor margin MVI 70% 69% 51% 83% 69%
Lee et al. [58] EOB-MRI Peritumoral hypointensity on HBP MVI 32% 92% 65% 74% 73%
Tada et al. [60] EOB-MRI Irregular tumor margin Non-SN type 97% 72% 74% 97% 83%
Chen et al. [61] EOB-MRI Irregular tumor margin Non-SN type 96% 79% 87% 94% 89%
Kobayashi et al. [62] EOB-MRI Irregular tumor margin Non-SN type 64% 96% 93% 77% 81%
Chen et al. [61] EOB-MRI + CECT Irregular tumor margin Non-SN type 98% 84% 90% 94% 93%
Kobayashi et al. [62] EOB-MRI + CEUS Irregular tumor margin Non-SN type 85% 95% 94% 88% 91%
PPV: positive predictive value; NPV: negative predictive value; MRI: magnetic resonance imaging; N/A: not available; ADC: apparent
diffusion coefficient; MVI: microvascular invasion; EOB-MRI: Gadolinium-ethoxybenzyl diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid-enhanced
magnetic resonance imaging; HBP: hepatobiliary phase; SN: single nodular; CECT: contrast enhanced computed tomography; CEUS:
contrast enhanced ultrasonography
[58]
were 38.3%, 93.2%, 88.5%, 52.6% and 62% respectively. Lee et al. also demonstrated that a combination of
two or more of the following; arterial peritumoral enhancement, irregular tumor margin, and peritumoral
hypointensity on hepatobiliary phase, can be used as a preoperative imaging biomarker for predicting MVI,
[59]
with specificity > 90%. Hu et al. also reported in a systemic review and meta-analysis that peritumoral
enhancement and peritumoral hypointensity on hepatobiliary phase were highly specific (90%-94%) but low
sensitive findings (29%-40%) for predicting MVI.
[60]
On distinguishing between the SN type and non-SN type using EOB-MRI, Tada et al. demonstrated
that the sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of EOB-MRI for identifying non-SN were equal to or higher
[61]
than that using angiography-assisted CT. Chen et al. also compared the diagnostic ability of EOB-MRI
and contrast CT. The sensitivities, specificities, and accuracies for the diagnosis of non-SN type were 71.4%,
81.6%, and 75.5% in contrast CT, 96.4%, 78.9%, and 89.3% in EOB-MRI, and 98.2%, 84.2%, and 92.5% in
combination, respectively. They concluded that contrast CT combined with EOB-MRI offers a more accurate
[62]
[61]
imaging evaluation for HCC macroscopic classification than either modality alone . Kobayashi et al.
compared the ability of EOB-MRI and CEUS to predict macroscopic type, and found that the sensitivity,
specificity, PPV, NPV, and accuracy for the diagnosis of non-SN type were 64.1%, 95.7%, 92.6%, 76.9% and
81.2% in EOB-MRI, 56.4%, 97.8%, 95.7%, 72.6% and 78.8% in CEUS, and 84.6%, 95.7%, 94.3%, 88% and 90.6%
in combination, respectively. The combined diagnosis of EOB-MRI and CEUS provides highest diagnostic
[62]
[63]
ability . Iwamoto et al. also showed that the diagnostic ability for macroscopic classification of nodular
HCC of the post-vascular phase of CEUS with Sonazoid was comparable with that of hepatobiliary phase of
EOB-MRI, and the combination of the two modalities provided a more accurate diagnostic performance.
The sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV, and accuracy of MRI studies cited in this review were summarized in
Table 3 except for not available reports.
DISCUSSION
This article reviews the current status of predicting MVI using common imaging modalities for the diag-
nosis of HCC. MVI is strongly associated with histologic differentiation and macroscopic type. Poorly dif-
ferentiated HCCs are characterized by hypovascular components and faster tumor enhancement washout on
dynamic imaging. Non-SN type HCCs are characterized by irregular shape image. The possible mechanism