Page 103 - Read Online
P. 103
Karademir. Hepatoma Res 2018;4:58 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2018.40 Page 13 of 18
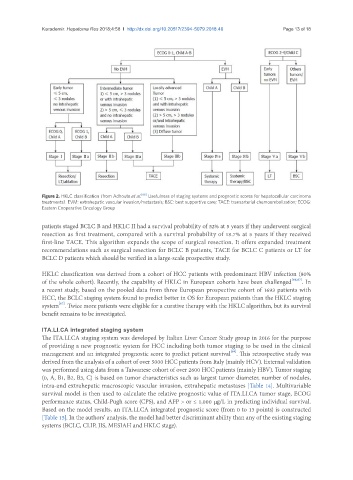
Figure 2. HKLC classification (from Adhoute et al. [66] Usefulness of staging systems and prognostic scores for hepatocellular carcinoma
treatments). EVM: extrahepatic vascular invasion/metastasis; BSC: best supportive care; TACE: transarterial chemoembolization; ECOG:
Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group
patients staged BCLC B and HKLC II had a survival probability of 52% at 5 years if they underwent surgical
resection as first treatment, compared with a survival probability of 18.7% at 5 years if they received
first-line TACE. This algorithm expands the scope of surgical resection. It offers expanded treatment
recommendations such as surgical resection for BCLC B patients, TACE for BCLC C patients or LT for
BCLC D patients which should be verified in a large-scale prospective study.
HKLC classification was derived from a cohort of HCC patients with predominant HBV infection (80%
of the whole cohort). Recently, the capability of HKLC in European cohorts have been challenged [66,67] . In
a recent study, based on the pooled data from three European prospective cohort of 1693 patients with
HCC, the BCLC staging system found to predict better in OS for European patients than the HKLC staging
[67]
system . Twice more patients were eligible for a curative therapy with the HKLC algorithm, but its survival
benefit remains to be investigated.
ITA.LI.CA integrated staging system
The ITA.LI.CA staging system was developed by Italian Liver Cancer Study group in 2016 for the purpose
of providing a new prognostic system for HCC including both tumor staging to be used in the clinical
[68]
management and an integrated prognostic score to predict patient survival . This retrospective study was
derived from the analysis of a cohort of over 5000 HCC patients from Italy (mainly HCV). External validation
was performed using data from a Taiwanese cohort of over 2600 HCC patients (mainly HBV). Tumor staging
(0, A, B1, B2, B3, C) is based on tumor characteristics such as largest tumor diameter, number of nodules,
intra-and extrahepatic macroscopic vascular invasion, extrahepatic metastases [Table 14]. Multivariable
survival model is then used to calculate the relative prognostic value of ITA.LI.CA tumor stage, ECOG
performance status, Child-Pugh score (CPS), and AFP > or ≤ 1,000 μg/L in predicting individual survival.
Based on the model results, an ITA.LI.CA integrated prognostic score (from 0 to 13 points) is constructed
[Table 15]. In the authors’ analysis, the model had better discriminant ability than any of the existing staging
systems (BCLC, CLIP, JIS, MESIAH and HKLC stage).