Page 165 - Read Online
P. 165
Bhatia et al. Hepatoma Res 2018;4:9 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2018.04 Page 7 of 16
A 50 Control B NDEA
50
45 45
40 40
35 35
Counts (%) 30 Liver Counts (%) 30
25
25
20
20
15 15 Liver
10 10
5 5
0 0
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65
t (in minutes) t (in minutes)
D LycT + NDEA
C 60
50 LycT
50
40
40
Counts (%) 30 Counts (%) 30 Liver
20
Liver 20
10 10
0 0
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65
t (in minutes) t (in minutes)
E 120 Control
100 NDEA
Hepatic mebrofebnin retention (% peak counts) 60 LycT
80
LycT + NDEA
40
20
0
PEAK 10 20 30 45 60
t (in minutes)
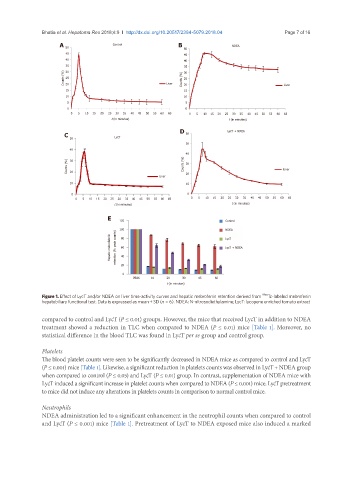
Figure 1. Effect of LycT and/or NDEA on liver time-activity curves and hepatic mebrofenin retention derived from 99m Tc-labeled mebrofenin
hepatobiliary functional test. Data is expressed as mean ± SD (n = 6). NDEA: N-nitrosodiethylamine; LycT: lycopene enriched tomato extract
compared to control and LycT (P ≤ 0.01) groups. However, the mice that received LycT in addition to NDEA
treatment showed a reduction in TLC when compared to NDEA (P ≤ 0.01) mice [Table 1]. Moreover, no
statistical difference in the blood TLC was found in LycT per se group and control group.
Platelets
The blood platelet counts were seen to be significantly decreased in NDEA mice as compared to control and LycT
(P ≤ 0.001) mice [Table 1]. Likewise, a significant reduction in platelets counts was observed in LycT + NDEA group
when compared to control (P ≤ 0.05) and LycT (P ≤ 0.01) group. In contrast, supplementation of NDEA mice with
LycT induced a significant increase in platelet counts when compared to NDEA (P ≤ 0.001) mice. LycT pretreatment
to mice did not induce any alterations in platelets counts in comparison to normal control mice.
Neutrophils
NDEA administration led to a significant enhancement in the neutrophil counts when compared to control
and LycT (P ≤ 0.001) mice [Table 1]. Pretreatment of LycT to NDEA exposed mice also induced a marked