Page 29 - Read Online
P. 29
Fung et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma rupture hepatectomy
Table 2: Post-operative outcomes and long-term follow-up data for post-hepatectomy patients, expressed as
medians with range
Emergency hepatectomy (n = 9) Interval hepatectomy (n = 21) P value
Complications
Wound infection 2 2 0.35
Pleural effusion 2 3 0.60
Pleural effusion requiring drainage 0 1 0.51
Confusion 0 1 0.12
Ascites 0 1 0.51
Total 4 (44%) 8 (38%) 0.53
Median hospital stay after hepatectomy (days) 10 (5-17) 12 (6-32) 0.07
30 day mortality rate 0 0 -
Time to intra-hepatic recurrence (months) 7.8 (2.6-100) 5.0 (1.1-39.5) 0.12
Time to extra-hepatic recurrence (months) 6.8 (6.4-8.9) 9.7 (4.0-47.9) 0.59
Peritoneal recurrence 1 (11%) 6 (29%) 0.27
Time to peritoneal recurrence (months) 6.4 6.4 (4.0-10.1) 0.55
Pulmonary recurrence 3 (33%) 4 (19%) 0.44
Time to pulmonary recurrence (months) 6.8 (6.4-8.9) 7.9 (4.0-12.2) 0.06
Recurrence in other location 0 4 (33%) 0.15
Time to other location recurrence (months) - 11.7 (10.1-47.8)
Time to earliest recurrence (months) 6.8 5.6 0.74
Overall survival (months) 29 (4-100) 15.7 (8-49) 0.25
1-year overall survival 7/9 (78%) 18/21 (85%) 0.59
3-year overall survival 4/9 (45%) 9/21 (43%) 0.94
5-year overall survival 0/9 (0%) 1/21 (5%) 0.51
A B
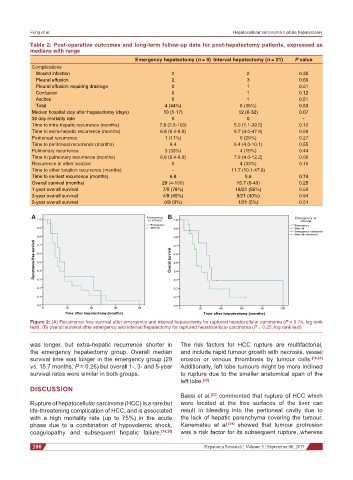
Figure 2: (A) Recurrence-free survival after emergency and interval hepatectomy for ruptured hepatocellular carcinoma (P = 0.74, log rank
test); (B) overall survival after emergency and interval hepatectomy for ruptured hepatocellular carcinoma (P = 0.25, log rank test)
was longer, but extra-hepatic recurrence shorter in The risk factors for HCC rupture are multifactorial,
the emergency hepatectomy group. Overall median and include rapid tumour growth with necrosis, vessel
survival time was longer in the emergency group (29 erosion or venous thrombosis by tumour cells. [16,21]
vs. 15.7 months, P = 0.26) but overall 1-, 3- and 5-year Additionally, left lobe tumours might be more inclined
survival rates were similar in both groups. to rupture due to the smaller anatomical span of the
left lobe. [22]
DISCUSSION
Bassi et al. [23] commented that rupture of HCC which
Rupture of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a rare but were located at the free surfaces of the liver can
life-threatening complication of HCC, and is associated result in bleeding into the peritoneal cavity due to
with a high mortality rate (up to 75%) in the acute the lack of hepatic parenchyma covering the tumour.
phase due to a combination of hypovolemic shock, Kanematsu et al. [24] showed that tumour protrusion
coagulopathy and subsequent hepatic failure. [19,20] was a risk factor for its subsequent rupture, whereas
200 Hepatoma Research ¦ Volume 3 ¦ September 08, 2017