Page 28 - Read Online
P. 28
Fung et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma rupture hepatectomy
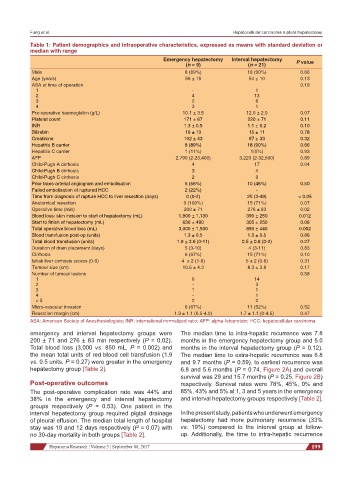
Table 1: Patient demographics and intraoperative characteristics, expressed as means with standard deviation or
median with range
Emergency hepatectomy Interval hepatectomy P value
(n = 9) (n = 21)
Male 8 (89%) 18 (90%) 0.66
Age (years) 56 ± 15 54 ± 10 0.13
ASA at time of operation 0.19
1 - 1
2 4 13
3 2 6
4 3 1
Pre-operative haemoglobin (g/L) 10.1 ± 3.5 12.0 ± 2.0 0.07
Platelet count 171 ± 67 220 ± 71 0.11
INR 1.3 ± 0.5 1.1 ± 0.2 0.10
Bilirubin 16 ± 13 15 ± 11 0.78
Creatinine 102 ± 43 87 ± 33 0.32
Hepatitis B carrier 8 (89%) 18 (90%) 0.66
Hepatitis C carrier 1 (11%) 1(5%) 0.93
AFP 2,790 (2-23,400) 3,220 (2-32,500) 0.89
Child-Pugh A cirrhosis 4 17 0.04
Child-Pugh B cirrhosis 3 4
Child-Pugh C cirrhosis 2 0
Prior trans-arterial angiogram and embolisation 5 (56%) 10 (48%) 0.50
Failed embolisation of ruptured HCC 2 (22%) -
Time from diagnosis of rupture HCC to liver resection (days) 0 (0-2) 25 (3-49) < 0.05
Anatomical resection 9 (100%) 15 (71%) 0.07
Operative time (min) 200 ± 71 276 ± 83 0.02
Blood loss: skin incision to start of hepatectomy (mL) 1,900 ± 1,130 390 ± 250 0.012
Start to finish of hepatectomy (mL) 630 ± 490 305 ± 250 0.06
Total operative blood loss (mL) 3,000 ± 1,500 850 ± 440 0.002
Blood transfusion post-op (units) 1.3 ± 0.5 1.3 ± 0.5 0.86
Total blood transfusion (units) 1.9 ± 3.6 (0-11) 0.5 ± 0.8 (0-2) 0.27
Duration of drain placement (days) 5 (3-10) 4 (3-11) 0.83
Cirrhosis 6 (67%) 15 (71%) 0.10
Ishak liver cirrhosis scores (0-6) 4 ± 2 (1-6) 5 ± 2 (0-6) 0.31
Tumour size (cm) 10.5 ± 4.3 8.3 ± 3.8 0.17
Number of tumour lesions 0.58
1 6 14
2 - 3
3 1 1
4 - 1
> 5 2 2
Micro-vascular invasion 6 (67%) 11 (52%) 0.52
Resection margin (cm) 1.3 ± 1.1 (0.5-4.0) 1.7 ± 1.1 (0-4.5) 0.47
ASA: American Society of Anesthesiologists; INR: international normalized ratio; AFP: alpha-fetoprotein; HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma
emergency and interval hepatectomy groups were The median time to intra-hepatic recurrence was 7.8
200 ± 71 and 276 ± 83 min respectively (P = 0.02). months in the emergency hepatectomy group and 5.0
Total blood loss (3,000 vs. 850 mL, P = 0.002) and months in the interval hepatectomy group (P = 0.12).
the mean total units of red blood cell transfusion (1.9 The median time to extra-hepatic recurrence was 6.8
vs. 0.5 units, P = 0.27) were greater in the emergency and 9.7 months (P = 0.59), to earliest recurrence was
hepatectomy group [Table 2]. 6.8 and 5.6 months (P = 0.74, Figure 2A) and overall
survival was 29 and 15.7 months (P = 0.25, Figure 2B)
Post-operative outcomes respectively. Survival rates were 78%, 45%, 0% and
The post-operative complication rate was 44% and 85%, 43% and 5% at 1, 3 and 5 years in the emergency
38% in the emergency and interval hepatectomy and interval hepatectomy groups respectively [Table 2].
groups respectively (P = 0.53). One patient in the
interval hepatectomy group required pigtail drainage In the present study, patients who underwent emergency
of pleural effusion. The median total length of hospital hepatectomy had more pulmonary recurrence (33%
stay was 10 and 12 days respectively (P = 0.07) with vs. 19%) compared to the interval group at follow-
no 30-day mortality in both groups [Table 2]. up. Additionally, the time to intra-hepatic recurrence
Hepatoma Research ¦ Volume 3 ¦ September 08, 2017 199