Page 27 - Read Online
P. 27
Fung et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma rupture hepatectomy
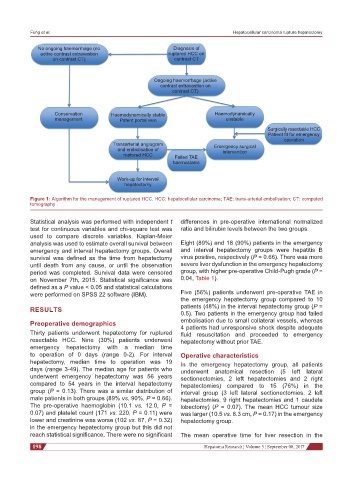
No ongoing haemorrhage (no Diagnosis of
active contrast extravastion ruptured HCC on
on contrast CT) contrast CT
Ongoing haemorrhage (active
contrast extravastion on
contrast CT)
Conservation Haemodynamically stable Haemodynamically
management Patent portal vein unstable
Surgically resectable HCC
Patient fit for emergency
operation
Transarterial angiogram Emergency surgical
and embolisation of intervention
ruptured HCC Failed TAE
haemostasis
Work-up for interval
hepatectomy
Figure 1: Algorithm for the management of ruptured HCC. HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; TAE: trans-arterial embolisation; CT: computed
tomography
Statistical analysis was performed with independent t differences in pre-operative international normalized
test for continuous variables and chi-square test was ratio and bilirubin levels between the two groups.
used to compare discrete variables. Kaplan-Meier
analysis was used to estimate overall survival between Eight (89%) and 18 (90%) patients in the emergency
emergency and interval hepatectomy groups. Overall and interval hepatectomy groups were hepatitis B
survival was defined as the time from hepatectomy virus positive, respectively (P = 0.66). There was more
until death from any cause, or until the observation severe liver dysfunction in the emergency hepatectomy
period was completed. Survival data were censored group, with higher pre-operative Child-Pugh grade (P =
on November 7th, 2015. Statistical significance was 0.04, Table 1).
defined as a P value < 0.05 and statistical calculations
were performed on SPSS 22 software (IBM). Five (56%) patients underwent pre-operative TAE in
the emergency hepatectomy group compared to 10
RESULTS patients (48%) in the interval hepatectomy group (P =
0.5). Two patients in the emergency group had failed
Preoperative demographics embolisation due to small collateral vessels, whereas
4 patients had unresponsive shock despite adequate
Thirty patients underwent hepatectomy for ruptured fluid resuscitation and proceeded to emergency
resectable HCC. Nine (30%) patients underwent hepatectomy without prior TAE.
emergency hepatectomy with a median time
to operation of 0 days (range 0-2). For interval Operative characteristics
hepatectomy, median time to operation was 19 In the emergency hepatectomy group, all patients
days (range 3-49). The median age for patients who underwent anatomical resection (5 left lateral
underwent emergency hepatectomy was 56 years sectionectomies, 2 left hepatectomies and 2 right
compared to 54 years in the interval hepatectomy hepatectomies) compared to 15 (76%) in the
group (P = 0.13). There was a similar distribution of interval group (3 left lateral sectionectomies, 2 left
male patients in both groups (89% vs. 90%, P = 0.66). hepatectomies, 9 right hepatectomies and 1 caudate
The pre-operative haemoglobin (10.1 vs. 12.0, P = lobectomy) (P = 0.07). The mean HCC tumour size
0.07) and platelet count (171 vs. 220, P = 0.11) were was larger (10.5 vs. 8.3 cm, P = 0.17) in the emergency
lower and creatinine was worse (102 vs. 87, P = 0.32) hepatectomy group.
in the emergency hepatectomy group but this did not
reach statistical significance. There were no significant The mean operative time for liver resection in the
198 Hepatoma Research ¦ Volume 3 ¦ September 08, 2017