Page 36 - Read Online
P. 36
Afyouni et al. Hepatoma Res 2023;9:28 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2023.29 Page 5 of 14
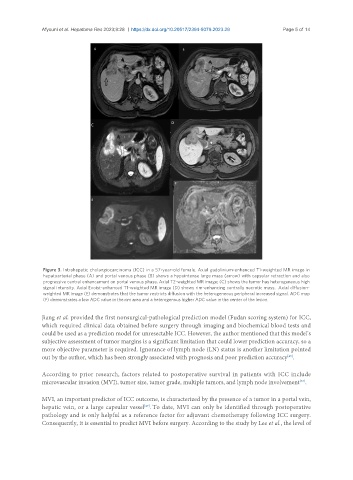
Figure 3. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) in a 57-year-old female. Axial gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted MR image in
hepatoarterial phase (A) and portal venous phase (B) shows a hypointense large mass (arrow) with capsular retraction and also
progressive central enhancement on portal venous phase. Axial T2-weighted MR image; (C) shows the tumor has heterogeneous high
signal intensity. Axial Evoist-enhanced T1-weighted MR image (D) shows rim-enhancing centrally necrotic mass. Axial diffusion-
weighted MR image (E) demonstrates that the tumor restricts diffusion with the heterogeneous peripheral increased signal. ADC map
(F) demonstrates a low ADC value in the rim area and a heterogenous higher ADC value in the center of the lesion.
Jiang et al. provided the first nonsurgical-pathological prediction model (Fudan scoring system) for ICC,
which required clinical data obtained before surgery through imaging and biochemical blood tests and
could be used as a prediction model for unresectable ICC. However, the author mentioned that this model’s
subjective assessment of tumor margins is a significant limitation that could lower prediction accuracy, so a
more objective parameter is required. Ignorance of lymph node (LN) status is another limitation pointed
out by the author, which has been strongly associated with prognosis and poor prediction accuracy .
[45]
According to prior research, factors related to postoperative survival in patients with ICC include
microvascular invasion (MVI), tumor size, tumor grade, multiple tumors, and lymph node involvement .
[46]
MVI, an important predictor of ICC outcome, is characterized by the presence of a tumor in a portal vein,
[47]
hepatic vein, or a large capsular vessel . To date, MVI can only be identified through postoperative
pathology and is only helpful as a reference factor for adjuvant chemotherapy following ICC surgery.
Consequently, it is essential to predict MVI before surgery. According to the study by Lee et al., the level of