Page 48 - Read Online
P. 48
Page 6 of 17 Sun et al. Chem Synth 2023;3:16 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cs.2022.45
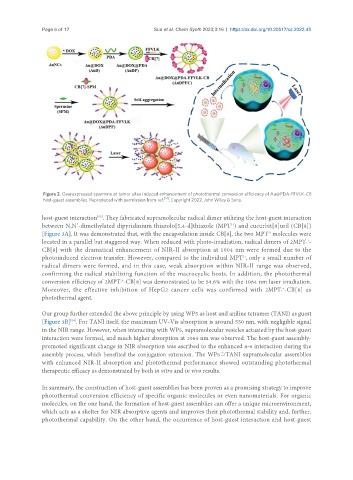
Figure 2. Overexpressed spermine at tumor sites induced enhancement of photothermal conversion efficiency of Au@PDA-FFVLK-CB
host-guest assemblies. Reproduced with permission from ref. [51] , Copyright 2022, John Wiley & Sons.
[53]
host-guest interaction . They fabricated supramolecular radical dimer utilizing the host-guest interaction
between N,N’-dimethylated dipyridinium thiazolo[5,4-d]thiazole (MPT ) and cucurbit[8]uril (CB[8])
2+
2+
[Figure 3A]. It was demonstrated that, with the encapsulation inside CB[8], the two MPT molecules were
located in a parallel but staggered way. When reduced with photo-irradiation, radical dimers of 2MPT· -
+
CB[8] with the dramatical enhancement of NIR-II absorption at 1004 nm were formed due to the
photoinduced electron transfer. However, compared to the individual MPT , only a small number of
2+
radical dimers were formed, and in this case, weak absorption within NIR-II range was observed,
confirming the radical stabilizing function of the macrocyclic hosts. In addition, the photothermal
conversion efficiency of 2MPT· -CB[8] was demonstrated to be 54.6% with the 1064 nm laser irradiation.
+
+
Moreover, the effective inhibition of HepG2 cancer cells was confirmed with 2MPT· -CB[8] as
photothermal agent.
Our group further extended the above principle by using WP5 as host and aniline tetramer (TANI) as guest
[54]
[Figure 3B] . For TANI itself, the maximum UV-Vis absorption is around 550 nm, with negligible signal
in the NIR range. However, when interacting with WP5, supramolecular vesicles actuated by the host-guest
interaction were formed, and much higher absorption at 1064 nm was observed. The host-guest assembly-
promoted significant change in NIR absorption was ascribed to the enhanced π-π interaction during the
assembly process, which benefited the conjugation extension. The WP5⊃TANI supramolecular assemblies
with enhanced NIR-II absorption and photothermal performance showed outstanding photothermal
therapeutic efficacy as demonstrated by both in vitro and in vivo results.
In summary, the construction of host-guest assemblies has been proven as a promising strategy to improve
photothermal conversion efficiency of specific organic molecules or even nanomaterials. For organic
molecules, on the one hand, the formation of host-guest assemblies can offer a unique microenvironment,
which acts as a shelter for NIR absorptive agents and improves their photothermal stability and, further,
photothermal capability. On the other hand, the occurrence of host-guest interaction and host-guest