Page 96 - Read Online
P. 96
Page 6 of 9 Wang et al. Chem Synth 2023;3:9 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cs.2022.44
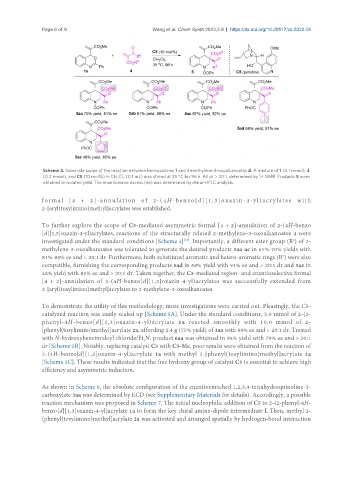
Scheme 4. Substrate scope of the reaction between benzoxazines 1 and 2-methylene-3-oxoalkanoates 4. A mixture of 1 (0.1 mmol), 4
1
(0.2 mmol), and C5 (10 mol%) in CH Cl (0.1 mL) was stirred at 35 °C for 96 h. All dr > 20:1, determined by H NMR. Products 5 were
2
2
obtained in isolated yield. The enantiomeric excess (ee) was determined by chiral-HPLC analysis.
f o r m a l [ 4 + 2 ] - a n n u l a t i o n o f 2 - ( 4 H - b e n z o [ d ] [ 1 , 3 ] o x a z i n - 4 - y l ) a c r y l a t e s w i t h
2-[aryl(tosylimino)methyl]acrylates was established.
To further explore the scope of C5-mediated asymmetric formal [4 + 2]-annulation of 2-(4H-benzo
[d][1,3]oxazin-4-yl)acrylates, reactions of the structurally related 2-methylene-3-oxoalkanoates 4 were
investigated under the standard conditions [Scheme 4] . Importantly, a different ester group (R ) of 2-
6
[18]
methylene-3-oxoalkanoates was tolerated to generate the desired products 5aa-ac in 61%-70% yields with
81%-88% ee and > 20:1 dr. Furthermore, both substituted aromatic and hetero-aromatic rings (R ) were also
5
compatible, furnishing the corresponding products 5ad in 68% yield with 91% ee and > 20:1 dr and 5ae in
48% yield with 85% ee and > 20:1 dr. Taken together, the C5-mediated region- and enantioselective formal
[4 + 2]-annulation of 2-(4H-benzo[d][1,3]oxazin-4-yl)acrylates was successfully extended from
2-[aryl(tosylimino)methyl]acrylates to 2-methylene-3-oxoalkanoates.
To demonstrate the utility of this methodology, more investigations were carried out. Pleasingly, the C5-
catalyzed reaction was easily scaled up [Scheme 5A]. Under the standard conditions, 5.0 mmol of 2-(2-
phenyl-4H-benzo[d][1,3]oxazin-4-yl)acrylate 1a reacted smoothly with 10.0 mmol of 2-
[phenyl(tosylimino)methyl]acrylate 2a, affording 2.4 g (75% yield) of 3aa with 89% ee and > 20:1 dr. Treated
with N-hydroxybenzimidoyl chloride/Et N, product 6aa was obtained in 96% yield with 79% ee and > 20:1
3
dr [Scheme 5B]. Notably, replacing catalyst C5 with C5-Me, poor results were obtained from the reaction of
2-(4H-benzo[d][1,3]oxazin-4-yl)acrylate 1a with methyl 2-[phenyl(tosylimino)methyl]acrylate 2a
[Scheme 5C]. These results indicated that the free hydroxy group of catalyst C5 is essential to achieve high
efficiency and asymmetric induction.
As shown in Scheme 6, the absolute configuration of the enantioenriched 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline-3-
carboxylate 3aa was determined by ECD (see Supplementary Materials for details). Accordingly, a possible
reaction mechanism was proposed in Scheme 7. The initial nucleophilic addition of C5 to 2-(2-phenyl-4H-
benzo[d][1,3]oxazin-4-yl)acrylate 1a to form the key chiral amine-dipole intermediate I. Then, methyl 2-
[phenyl(tosylimino)methyl]acrylate 2a was activated and arranged spatially by hydrogen-bond interaction