Page 71 - Read Online
P. 71
Page 247 Nickoloff et al. Cancer Drug Resist 2021;4:244-63 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2020.89
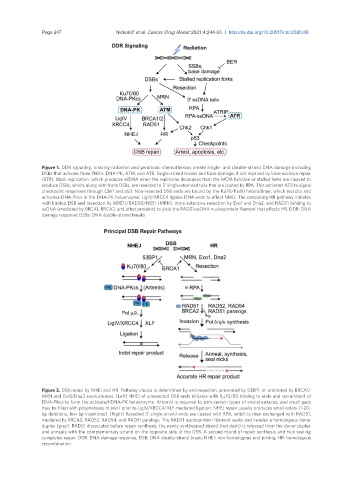
Figure 1. DDR signaling. Ionizing radiation and genotoxic chemotherapy create single- and double-strand DNA damage including
DSBs that activate three PIKKs: DNA-PK, ATM, and ATR. Single-strand breaks and base damage, if not repaired by base excision repair
(BER), block replication, which produces ssDNA when the replisome decouples from the MCM helicase or stalled forks are cleaved to
produce DSBs, which, along with frank DSBs, are resected to 3’ single-stranded tails that are coated by RPA. This activates ATR to signal
checkpoint responses through Chk1 and p53. Non-resected DSB ends are bound by the Ku70/Ku80 heterodimer, which recruits and
activates DNA-PKcs in the DNA-PK holoenzyme, LigIV/XRCC4 ligates DNA ends to effect NHEJ. The competing HR pathway initiates
with limited DSB end resection by MRE11/RAD50/NBS1 (MRN), more extensive resection by Exo1 and Dna2, and RAD51 binding to
ssDNA (mediated by BRCA1, BRCA2, and other proteins) to yield the RAD51-ssDNA nucleoprotein filament that effects HR. DDR: DNA
damage response; DSBs: DNA double-strand breaks
Figure 2. DSB repair by NHEJ and HR. Pathway choice is determined by end-resection, prevented by 53BP1, or promoted by BRCA1/
MRN and Exo1/Dna2 exonucleases. (Left) NHEJ of unresected DSB ends initiates with Ku70/80 binding to ends and recruitment of
DNA-PKcs to form the activated DNA-PK holoenzyme. Artemis is required to trim certain types of end-structures, and small gaps
may be filled with polymerases m and l prior to LigIV/XRCC4/XLF-mediated ligation. NHEJ repair usually produces small indels (1-20-
bp deletions, few-bp insertions). (Right) Resected 3’ single-strand ends are coated with RPA, which is then exchanged with RAD51,
mediated by BRCA2, RAD52, RAD54, and RAD51 paralogs. The RAD51 nucleoprotein filament seeks and invades a homologous donor
duplex (grey). RAD51 dissociates before repair synthesis; the newly synthesized strand (red dash) is released from the donor duplex
and anneals with the complementary strand on the opposite side of the DSB. A second round of repair synthesis and nick sealing
completes repair. DDR: DNA damage response; DSB: DNA double-strand break; NHEJ: non-homologous end-joining; HR: homologous
recombination