Page 67 - Read Online
P. 67
Raczka et al. Cancer Drug Resist 2019;2:356-64 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2018.004 Page 359
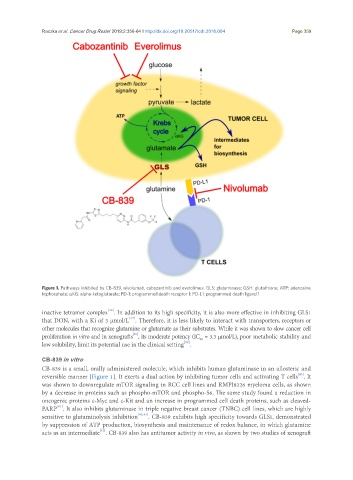
Figure 1. Pathways inhibited by CB-839, nivolumab, cabozantinib and everolimus. GLS: glutaminase; GSH: glutathione; ATP: adenosine
triphosphate; αKG: alpha-ketoglutarate; PD-1: programmed death receptor 1; PD-L1: programmed death ligand 1
[36]
inactive tetramer complex . In addition to its high specificity, it is also more effective in inhibiting GLS1
[37]
that DON, with a Ki of 3 µmol/L . Therefore, it is less likely to interact with transporters, receptors or
other molecules that recognize glutamine or glutamate as their substrates. While it was shown to slow cancer cell
[38]
proliferation in vitro and in xenografts , its moderate potency (IC = 3.3 μmol/L), poor metabolic stability and
50
[39]
low solubility, limit its potential use in the clinical setting .
CB-839 in vitro
CB-839 is a small, orally administered molecule, which inhibits human glutaminase in an allosteric and
[40]
reversible manner [Figure 1]. It exerts a dual action by inhibiting tumor cells and activating T cells . It
was shown to downregulate mTOR signaling in RCC cell lines and RMPI8226 myeloma cells, as shown
by a decrease in proteins such as phospho-mTOR and phospho-S6. The same study found a reduction in
oncogenic proteins c-Myc and c-Kit and an increase in programmed cell death proteins, such as cleaved-
[41]
PARP . It also inhibits glutaminase in triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) cell lines, which are highly
sensitive to glutaminolysis inhibition [42,43] . CB-839 exhibits high specificity towards GLS1, demonstrated
by suppression of ATP production, biosynthesis and maintenance of redox balance, in which glutamine
[42]
acts as an intermediate . CB-839 also has antitumor activity in vivo, as shown by two studies of xenograft