Page 50 - Read Online
P. 50
Sale et al. Cancer Drug Resist 2019;2:365-80 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2019.14 Page 367
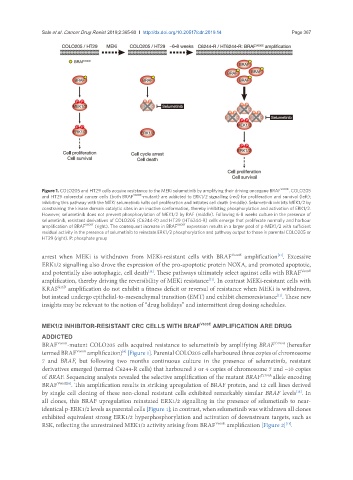
Figure 1. COLO205 and HT29 cells acquire resistance to the MEKi selumetinib by amplifying their driving oncogene BRAF V600E . COLO205
and HT29 colorectal cancer cells (both BRAF V600E -mutant) are addicted to ERK1/2 signalling (red) for proliferation and survival (left);
inhibiting this pathway with the MEKi selumetinib halts cell proliferation and initiates cell death (middle). Selumetinib inhibits MEK1/2 by
constraining the kinase domain catalytic sites in an inactive conformation, thereby inhibiting phosphorylation and activation of ERK1/2.
However, selumetinib does not prevent phosphorylation of MEK1/2 by RAF (middle). Following 6-8 weeks culture in the presence of
selumetinib, resistant derivatives of COLO205 (C6244-R) and HT29 (HT6244-R) cells emerge that proliferate normally and harbour
amplification of BRAF V600E (right). The consequent increase in BRAF V600E expression results in a larger pool of p-MEK1/2 with sufficient
residual activity in the presence of selumetinib to reinstate ERK1/2 phosphorylation and pathway output to those in parental COLO205 or
HT29 (right). P: phosphate group
arrest when MEKi is withdrawn from MEKi-resistant cells with BRAF V600E amplification . Excessive
[11]
ERK1/2 signalling also drove the expression of the pro-apoptotic protein NOXA, and promoted apoptotic,
and potentially also autophagic, cell death . These pathways ultimately select against cells with BRAF V600E
[11]
amplification, thereby driving the reversibility of MEKi resistance . In contrast MEKi-resistant cells with
[11]
KRAS G13D amplification do not exhibit a fitness deficit or reversal of resistance when MEKi is withdrawn,
but instead undergo epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and exhibit chemoresistance . These new
[11]
insights may be relevant to the notion of “drug holidays” and intermittent drug dosing schedules.
MEK1/2 INHIBITOR-RESISTANT CRC CELLS WITH BRAF V600E AMPLIFICATION ARE DRUG
ADDICTED
BRAF V600E -mutant COLO205 cells acquired resistance to selumetinib by amplifying BRAF T1799A (hereafter
termed BRAF V600E amplification) [Figure 1]. Parental COLO205 cells harboured three copies of chromosome
[9]
7 and BRAF, but following two months continuous culture in the presence of selumetinib, resistant
derivatives emerged (termed C6244-R cells) that harboured 3 or 4 copies of chromosome 7 and ~10 copies
of BRAF. Sequencing analysis revealed the selective amplification of the mutant BRAF T1799A allele encoding
BRAF V600E[9] . This amplification results in striking upregulation of BRAF protein, and 12 cell lines derived
by single cell cloning of these non-clonal resistant cells exhibited remarkably similar BRAF levels . In
[11]
all clones, this BRAF upregulation reinstated ERK1/2 signalling in the presence of selumetinib to near-
identical p-ERK1/2 levels as parental cells [Figure 1]; in contrast, when selumetinib was withdrawn all clones
exhibited equivalent strong ERK1/2 hyperphosphorylation and activation of downstream targets, such as
RSK, reflecting the unrestrained MEK1/2 activity arising from BRAF V600E amplification [Figure 2] .
[11]