Page 81 - Read Online
P. 81
De Mattia et al. Cancer Drug Resist 2019;2:116-30 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2019.04 Page 123
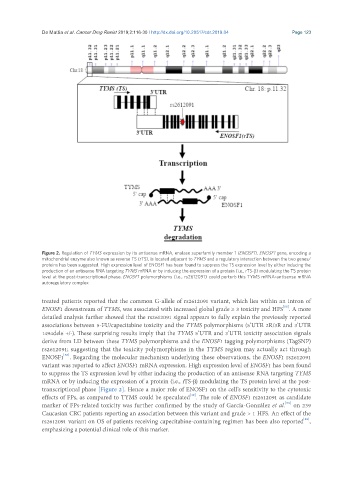
Figure 2. Regulation of TYMS expression by its antisense mRNA, enolase superfamily member 1 (ENOSF1). ENOSF1 gene, encoding a
mitochondrial enzyme also known as reverse TS (rTS), is located adjacent to TYMS and a regulatory interaction between the two genes/
proteins has been suggested. High expression level of ENOSF1 has been found to suppress the TS expression level by either inducing the
production of an antisense RNA targeting TYMS mRNA or by inducing the expression of a protein (i.e., rTS-β) modulating the TS protein
level at the post-transcriptional phase. ENOSF1 polymorphisms (i.e., rs2612091) could perturb this TYMS mRNA-antisense mRNA
autoregulatory complex
treated patients reported that the common G-allele of rs2612091 variant, which lies within an intron of
[58]
ENOSF1 downstream of TYMS, was associated with increased global grade ≥ 3 toxicity and HFS . A more
detailed analysis further showed that the rs2612091 signal appears to fully explain the previously reported
associations between 5-FU/capecitabine toxicity and the TYMS polymorphisms (5’UTR 2R/3R and 3’UTR
1494del6 +/-). These surprising results imply that the TYMS 5’UTR and 3’UTR toxicity association signals
derive from LD between these TYMS polymorphisms and the ENOSF1 tagging polymorphisms (TagSNP)
rs2612091; suggesting that the toxicity polymorphisms in the TYMS region may actually act through
[58]
ENOSF1 . Regarding the molecular mechanism underlying these observations, the ENOSF1 rs2612091
variant was reported to affect ENOSF1 mRNA expression. High expression level of ENOSF1 has been found
to suppress the TS expression level by either inducing the production of an antisense RNA targeting TYMS
mRNA or by inducing the expression of a protein (i.e., rTS-β) modulating the TS protein level at the post-
transcriptional phase [Figure 2]. Hence a major role of ENOSF1 on the cell’s sensitivity to the cytotoxic
[49]
effects of FPs, as compared to TYMS could be speculated . The role of ENOSF1 rs2612091 as candidate
[59]
marker of FPs-related toxicity was further confirmed by the study of García-González et al. on 239
Caucasian CRC patients reporting an association between this variant and grade > 1 HFS. An effect of the
[49]
rs2612091 variant on OS of patients receiving capecitabine-containing regimen has been also reported ,
emphasizing a potential clinical role of this marker.