Page 153 - Read Online
P. 153
Page 168 Kumar et al. Cancer Drug Resist 2019;2:161-77 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2018.27
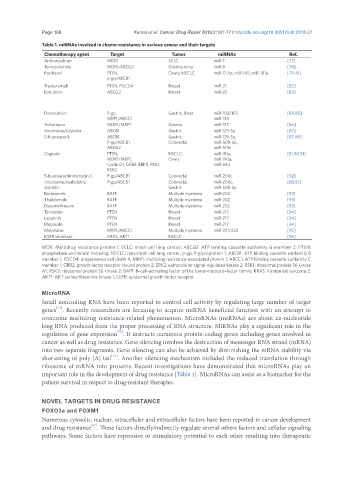
Table 1. miRNAs involved in chemo-resistance in various cancer and their targets
Chemotherapy agent Target Tumor miRNAs Ref.
Anthracyclines MDR1 SCLC miR-7 [77]
Temozolomide MDR1/ABCG2 Glioblastoma miR-9 [78]
Paclitaxel PTEN, Ovary, NSCLC miR-17-5p, miR-145, miR-181a [79-81]
p-gp/ABCB1
Trastuzumab PTEN, PDCD4 Breast miR-21 [82]
Epriubicin ABCG2 Breast miR-25 [83]
Doxorubicin P-gp, Gastric, Brest miR-103/107, [84,85]
MRP1/ABCC1 miR-134
Adriamycin MDR1/MRP1 Glioma miR-127 [86]
Vincristine/cisplatin ABCB1 Gastric miR-129-5p [87]
5-fluorouracil ABCB1, Gastric, miR-129-5p, [87-89]
P-gp/ABCB1, Colorectal miR-508-5p,
ABCG2 miR-519c
Cisplatin PTEN, NSCLC, miR-181a, [81,90,91]
MDR1/MRP1, Ovary miR-196a,
Cyclin D1, GRB2, ERK2, RSK1, miR-634
RSK2
5-fluorouracilmitomycin C P-gp/ABCB1 Colorectal miR-200c [92]
Vincristine/oxaliplatin/ P-gp/ABCB1 Colorectal, miR-200c, [88,92]
cisplatin Gastric miR-508-5p
Bortezomib BAFF Multiple myeloma miR-202 [93]
Thalidomide BAFF Multiple myeloma miR-202 [93]
Dexamethasone BAFF Multiple myeloma miR-202 [93]
Tamoxifen PTEN Breast miR-217 [94]
Lapatinib PTEN Breast miR-217 [94]
Etoposide PTEN Breast miR-217 [94]
Melphalan MRP1/ABCC1 Multiple myeloma miR-221/222 [95]
EGFR inhibitors KRAS, AKT1 NSCLC [96]
MDR: Multidrug resistance protein 1; SCLC: small cell lung cancer; ABCG2: ATP binding cassette subfamily G member 2; PTEN:
phosphatase and tensin homolog; NSCLC: non-small cell lung cancer; p-gp: P-glycoprotein 1; ABCB1: ATP binding cassette subfamily B
member 1; PDCD4: programmed cell death 4; MRP1: multidrug resistance-associated protein 1; ABCC1: ATP binding cassette subfamily C
member 1; GRB2: growth factor receptor-bound protein 2; ERK2: extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2; RSK1: ribosomal protein S6 kinase
A1; RSK2: ribosomal protein S6 kinase 2; BAFF: B-cell-activating factor of the tumor-necrosis-factor family; KRAS: Kirsten rat sarcoma 2;
AKT1: AKT serine/threonine kinase 1; EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor
MicroRNA
Small noncoding RNA have been reported to control cell activity by regulating large number of target
[74]
genes . Recently researchers are focusing to acquire miRNA beneficial function with an attempt to
overcome multidrug resistance-related phenomenon. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are about 22-nucleotide
long RNA produced from the proper processing of RNA structure. MiRNAs play a significant role in the
[75]
regulation of gene expression . It instructs numerous protein-coding genes including genes involved in
cancer as well as drug resistance. Gene silencing involves the destruction of messenger RNA strand (mRNA)
into two separate fragments. Gene silencing can also be achieved by diminishing the mRNA stability via
[76]
shortening of poly (A) tail . Another silencing mechanism included the reduced translation through
ribosome of mRNA into proteins. Recent investigations have demonstrated that microRNAs play an
important role in the development of drug resistance [Table 1]. MicroRNAs can assist as a biomarker for the
patient survival in respect to drug-resistant therapies.
NOVEL TARGETS IN DRUG RESISTANCE
FOXO3a and FOXM1
Numerous cytosolic, nuclear, intracellular and extracellular factors have been reported in cancer development
[97]
and drug resistance . These factors directly/indirectly regulate several others factors and cellular signaling
pathways. Some factors have repressive or stimulatory potential to each other resulting into therapeutic