Page 149 - Read Online
P. 149
Page 164 Kumar et al. Cancer Drug Resist 2019;2:161-77 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2018.27
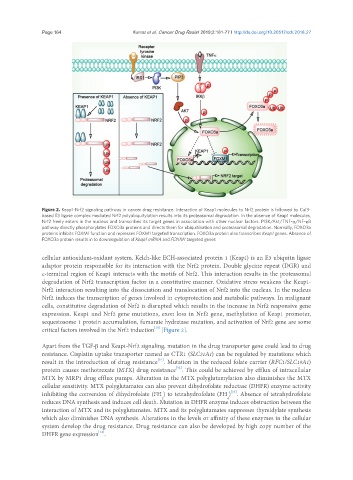
Figure 2. Keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathway in cancer drug resistance. Interaction of Keap1 molecules to Nrf2 protein is followed by Cul3-
based E3 ligase complex mediated Nrf2 polyubiquitylation results into its proteasomal degradation. In the absence of Keap1 molecules,
Nrf2 freely enters in the nucleus and transcribes its target genes in association with other nuclear factors. PI3K/Akt/TNF-α/NF-κB
pathway directly phosphorylates FOXO3a proteins and directs them for ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. Normally, FOXO3a
proteins inhibits FOXM1 function and represses FOXM1 targeted transcription. FOXO3a protein also transcribes Keap1 genes. Absence of
FOXO3a protein results in to downregulation of Keap1 mRNA and FOXM1 targeted genes
cellular antioxidant-oxidant system. Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1) is an E3 ubiquitn ligase
adaptor protein responsible for its interaction with the Nrf2 protein. Double glycine repeat (DGR) and
c-terminal region of Keap1 interacts with the motifs of Nrf2. This interaction results in the proteasomal
degradation of Nrf2 transcription factor in a constitutive manner. Oxidative stress weakens the Keap1-
Nrf2 interaction resulting into the dissociation and translocation of Nrf2 into the nucleus. In the nucleus
Nrf2 induces the transcription of genes involved in cytoprotection and metabolic pathways. In malignant
cells, constitutive degradation of Nrf2 is disrupted which results in the increase in Nrf2 responsive gene
expression. Keap1 and Nrf2 gene mutations, exon loss in Nrf2 gene, methylation of Keap1 promoter,
sequestosome 1 protein accumulation, fumarate hydratase mutation, and activation of Nrf2 gene are some
[30]
critical factors involved in the Nrf2 induction [Figure 2].
Apart from the TGF-β and Keap1-Nrf2 signaling, mutation in the drug transporter gene could lead to drug
resistance. Cisplatin uptake transporter named as CTR1 (SLC31A1) can be regulated by mutations which
[31]
result in the introduction of drug resistance . Mutation in the reduced folate carrier (RFC1/SLC19A1)
[32]
protein causes methotrexate (MTX) drug resistance . This could be achieved by efflux of intracellular
MTX by MRP1 drug efflux pumps. Alteration in the MTX polyglutamylation also diminishes the MTX
cellular sensitivity. MTX polyglutamates can also prevent dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) enzyme activity
[33]
inhibiting the conversion of dihydrofolate (FH ) to tetrahydrofolate (FH ) . Absence of tetrahydrofolate
2
4
reduces DNA synthesis and induces cell death. Mutation in DHFR enzyme induces obstruction between the
interaction of MTX and its polyglutamates. MTX and its polyglutamates suppresses thymidylate synthesis
which also diminishes DNA synthesis. Alterations in the levels or affinity of these enzymes in the cellular
system develop the drug resistance. Drug resistance can also be developed by high copy number of the
[34]
DHFR gene expression .