Page 28 - Read Online
P. 28
Page 4 of 14 Xu et al. Cancer Drug Resist 2024;7:13 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2023.141
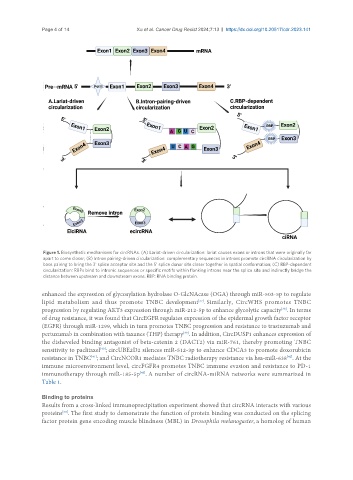
Figure 1. Biosynthetic mechanisms for circRNAs. (A) Lariat-driven circularization: lariat causes exons or introns that were originally far
apart to come closer; (B) Intron pairing-driven circularization: complementary sequences in introns promote circRNA circularization by
base pairing to bring the 3' splice acceptor site and the 5' splice donor site closer together in spatial conformation; (C) RBP-dependent
circularization: RBPs bind to intronic sequences or specific motifs within flanking introns near the splice site and indirectly bridge the
distance between upstream and downstream exons. RBP: RNA binding protein.
enhanced the expression of glycosylation hydrolase O-GlcNAcase (OGA) through miR-503-5p to regulate
lipid metabolism and thus promote TNBC development . Similarly, CircWHS promotes TNBC
[37]
progression by regulating AKT3 expression through miR-212-5p to enhance glycolytic capacity . In terms
[38]
of drug resistance, it was found that CircEGFR regulates expression of the epidermal growth factor receptor
(EGFR) through miR-1299, which in turn promotes TNBC progression and resistance to trastuzumab and
pertuzumab in combination with taxanes (THP) therapy . In addition, CircDUSP1 enhances expression of
[39]
the disheveled binding antagonist of beta-catenin 2 (DACT2) via miR-761, thereby promoting TNBC
[40]
sensitivity to paclitaxel ; circUBE2D2 silences miR-512-3p to enhance CDCA3 to promote doxorubicin
resistance in TNBC ; and CircNCOR1 mediates TNBC radiotherapy resistance via hsa-miR-638 . At the
[42]
[41]
immune microenvironment level, circFGFR4 promotes TNBC immune evasion and resistance to PD-1
immunotherapy through miR-185-5p . A number of circRNA-miRNA networks were summarized in
[43]
Table 1.
Binding to proteins
Results from a cross-linked immunoprecipitation experiment showed that circRNA interacts with various
proteins . The first study to demonstrate the function of protein binding was conducted on the splicing
[68]
factor protein gene encoding muscle blindness (MBL) in Drosophila melanogaster, a homolog of human