Page 84 - Read Online
P. 84
Page 232 Van Der Steen et al. Cancer Drug Resist 2018;1:230-49 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2018.13
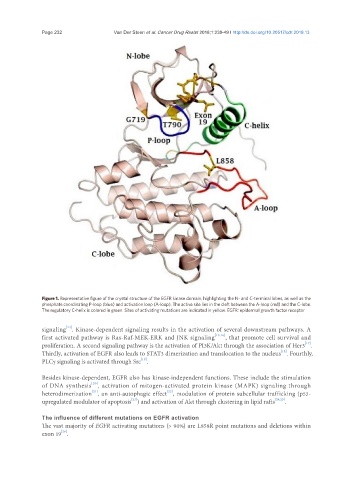
Figure 1. Representative figure of the crystal structure of the EGFR kinase domain, highlighting the N- and C-terminal lobes, as well as the
phosphate coordinating P-loop (blue) and activation loop (A-loop). The active site lies in the cleft between the A-loop (red) and the C-lobe.
The regulatory C-helix is colored in green. Sites of activating mutations are indicated in yellow. EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor
[14]
signaling . Kinase-dependent signaling results in the activation of several downstream pathways. A
first activated pathway is Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK and JNK signaling [15,16] , that promote cell survival and
[17]
proliferation. A second signaling pathway is the activation of PI3K/Akt through the association of Her3 .
[18]
Thirdly, activation of EGFR also leads to STAT3 dimerization and translocation to the nucleus . Fourthly,
[19]
PLCγ signaling is activated through Src .
Besides kinase-dependent, EGFR also has kinase-independent functions. These include the stimulation
[20]
of DNA synthesis , activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling through
[22]
[21]
heterodimerization , an anti-autophagic effect , modulation of protein subcellular trafficking (p53-
[23]
upregulated modulator of apoptosis ) and activation of Akt through clustering in lipid rafts [24,25] .
The influence of different mutations on EGFR activation
The vast majority of EGFR activating mutations (> 90%) are L858R point mutations and deletions within
[26]
exon 19 .