Page 118 - Read Online
P. 118
Page 773 Wong et al. Cancer Drug Resist 2023;6:768-87 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2023.58
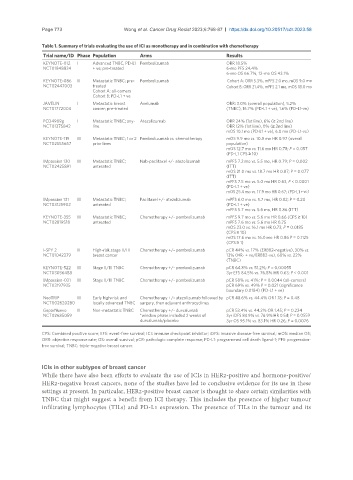
Table 1. Summary of trials evaluating the use of ICI as monotherapy and in combination with chemotherapy
Trial name/ID Phase Population Arms Results
KEYNOTE-012 I Advanced TNBC, PD-L1 Pembrolizumab ORR 18.5%
NCT01848834 + ve; pre-treated 6-mo PFS 24.4%
6-mo OS 66.7%, 12-mo OS 43.1%
KEYNOTE-086 II Metastatic TNBC; pre- Pembrolizumab Cohort A: ORR 5.3%, mPFS 2.0 mo, mOS 9.0 mo
NCT02447003 treated Cohort B: ORR 21.4%, mPFS 2.1 mo, mOS 18.0 mo
Cohort A: all-comers
Cohort B: PD-L1 + ve
JAVELIN I Metastatic breast Avelumab ORR: 3.0% (overall population), 5.2%
NCT01772004 cancer; pre-treated (TNBC), 16.7% (PD-L1 + ve), 1.6% (PD-L1-ve)
PCD4989g I Metastatic TNBC; any- Atezolizumab ORR 24% (1st line), 6% (≥ 2nd line)
NCT01375842 line ORR 12% (1st line), 0% (≥ 2nd line)
mOS 10.1 mo (PD-L1 + ve), 6.0 mo (PD-L1-ve)
KEYNOTE-119 III Metastatic TNBC; 1 or 2 Pembrolizumab vs. chemotherapy mOS 9.9 mo vs. 10.8 mo HR 0.97 (overall
NCT02555657 prior lines population)
mOS 12.7 mo vs. 11.6 mo HR 0.78; P = 0.057
(PD-L1 CPS ≥ 10)
IMpassion 130 III Metastatic TNBC; Nab-paclitaxel +/- atezolizumab mPFS 7.2 mo vs. 5.5 mo, HR 0.79; P = 0.002
NCT02425891 untreated (ITT)
mOS 21.0 mo vs. 18.7 mo HR 0.87; P = 0.077
(ITT)
mPFS 7.5 mo vs. 5.0 mo HR 0.63, P < 0.0001
(PD-L1 + ve)
mOS 25.4 mo vs. 17.9 mo HR 0.67; (PD-L1 + ve)
IMpassion 131 III Metastatic TNBC; Paclitaxel +/- atezolizumab mPFS 6.0 mo vs. 5.7 mo, HR 0.82; P = 0.20
NCT03125902 untreated (PD-L1 + ve)
mPFS 5.7 mo vs. 5.6 mo, HR 0.86 (ITT)
KEYNOTE-355 III Metastatic TNBC; Chemotherapy +/- pembrolizumab mPFS 9.7 mo vs. 5.6 mo HR 0.66 (CPS ≥ 10)
NCT02819518 untreated mPFS 7.6 mo vs. 5.6 mo HR 0.75
mOS 23.0 vs. 16.1 mo HR 0.73; P = 0.0185
(CPS ≥ 10)
mOS 17.6 mo vs. 16.0 mo HR 0.86 P = 0.1125
(CPS ≥ 1)
I-SPY 2 II High-risk stage II/III Chemotherapy +/- pembrolizumab pCR 44% vs. 17% (ERBB2-negative), 30% vs.
NCT01042379 breast cancer 13% (HR- + ve/ERBB2-ve), 60% vs. 22%
(TNBC)
KEYNOTE-522 III Stage II/III TNBC Chemotherapy +/- pembrolizumab pCR 64.8% vs. 51.2%; P = 0.00055
NCT03036488 3yr EFS 84.5% vs. 76.8% HR 0.63; P < 0.001
IMpassion-031 III Stage II/III TNBC Chemotherapy +/- pembrolizumab pCR 58% vs. 41%; P = 0.0044 (all-comers)
NCT03197935 pCR 69% vs. 49% P = 0.021 (significance
boundary 0.0184) (PD-L1 + ve)
NeoTRIP III Early high-risk and Chemotherapy +/- atezolizumab followed by pCR 48.6% vs. 44.4% OR 1.18; P = 0.48
NCT002620280 locally advanced TNBC surgery, then adjuvant anthracyclines
GeparNuevo II Non-metastatic TNBC Chemotherapy +/- durvalumab pCR 53.4% vs. 44.2% OR 1.45; P = 0.224
NCT02685059 *window phase included 2 weeks of 3yr iDFS 84.9% vs. 76.9% HR 0.54; P = 0.0559
durvalumab/placebo 3yr OS 95.1% vs. 83.1% HR 0.26; P = 0.0076
CPS: Combined positive score; EFS: event-free survival; ICI: immune checkpoint inhibitor; iDFS: invasive disease-free survival; mOS: median OS;
ORR: objective response rate; OS: overall survival; pCR: pathologic complete response; PD-L1: programmed cell death ligand-1; PFS: progression-
free survival; TNBC: triple-negative breast cancer.
ICIs in other subtypes of breast cancer
While there have also been efforts to evaluate the use of ICIs in HER2-positive and hormone-positive/
HER2-negative breast cancers, none of the studies have led to conclusive evidence for its use in these
settings at present. In particular, HER2-positive breast cancer is thought to share certain similarities with
TNBC that might suggest a benefit from ICI therapy. This includes the presence of higher tumour
infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) and PD-L1 expression. The presence of TILs in the tumour and its