Page 62 - Read Online
P. 62
Page 16 of 29 Novati et al. Ageing Neur Dis 2022;2:17 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/and.2022.19
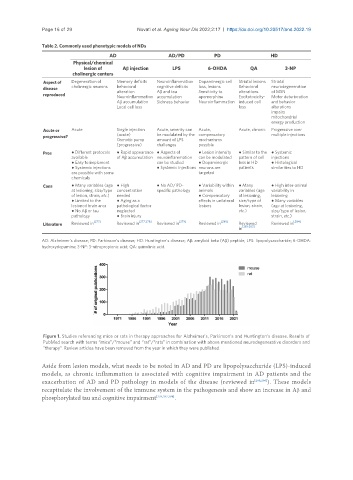
Table 2. Commonly used phenotypic models of NDs
AD AD/PD PD HD
Physical/chemical
lesion of Aβ injection LPS 6-OHDA QA 3-NP
cholinergic centers
Aspect of Degeneration of Memory deficits Neuroinflammation Dopaminergic cell Striatal lesions Striatal
disease cholinergic neurons behavioral cognitive deficits loss, lesions Behavioral neurodegeneration
reproduced alteration Aβ and tau Sensitivity to alterations of MSN
Neuroinflammation accumulation apomorphine Excitotoxicity- Motor deterioration
Aβ accumulation Sickness behavior Neuroinflammation induced cell and behavior
Local cell loss loss alterations
impairs
mitochondrial
energy production
Acute or Acute Single injection Acute, severity can Acute, Acute, chronic Progressive over
progressive? (acute) be modulated by the compensatory multiple injections
Osmotic pump amount of LPS mechanisms
(progressive) challenges possible
Pros ● Different protocols ● Rapid appearance ● Aspects of ● Lesion intensity ● Similar to the ● Systemic
available of Aβ accumulation neuroinflammation can be modulated pattern of cell injections
● Easy to implement can be studied ● Dopaminergic loss in HD ● Histological
● Systemic injections ● Systemic injections neurons are patients similarities to HD
are possible with some targeted
chemicals
Cons ● Many variables (age ● High ● No AD/ PD- ● Variability within ● Many ● High inter-animal
at lesioning, size/type concentration specific pathology animals variables (age variability in
of lesion, strain, etc.) needed ● Compensatory at lesioning, lesioning
● Limited to the ● Aging as a effects in unilateral size/type of ● Many variables
lesioned brain area pathological factor lesions lesion, strain, (age at lesioning,
● No Aβ or tau neglected etc.) size/type of lesion,
pathology ● Brain injury strain, etc.)
[277] [277,278] [279] [280] [284]
Literature Reviewed in Reviewed in Reviewed in Reviewed in Reviewed Reviewed in
in [281-283]
AD: Alzheimer’s disease; PD: Parkinson’s disease; HD: Huntington’s disease; Aβ: amyloid beta (Aβ) peptide; LPS: lipopolysaccharide; 6-OHDA:
hydroxydopamine; 3-NP: 3-nitropropionic acid; QA: quinolinic acid.
Figure 1. Studies referencing mice or rats in therapy approaches for Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s and Huntington’s disease. Results of
PubMed search with terms “mice”/“mouse” and “rat”/“rats” in combination with above mentioned neurodegenerative disorders and
“therapy”. Review articles have been removed from the year in which they were published.
Aside from lesion models, what needs to be noted in AD and PD are lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced
models, as chronic inflammation is associated with cognitive impairment in AD patients and the
exacerbation of AD and PD pathology in models of the disease (reviewed in [295,296] ). These models
recapitulate the involvement of the immune system in the pathogenesis and show an increase in Aβ and
phosphorylated tau and cognitive impairment [279,297,298] .