Page 51 - Read Online
P. 51
Novati et al. Ageing Neur Dis 2022;2:17 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/and.2022.19 Page 5 of 29
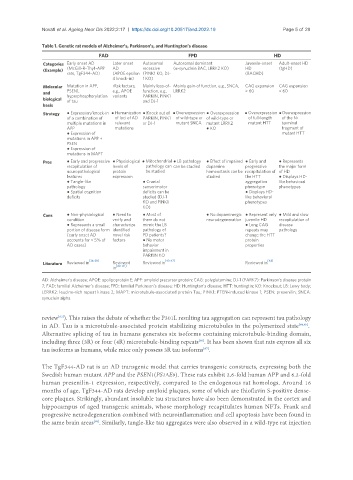
Table 1. Genetic rat models of Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and Huntington’s disease
FAD FPD HD
Categories Early onset AD Later onset Autosomal Autosomal dominant Juvenile-onset Adult-onset HD
(Example) (McGill-R-Thy1-APP AD recessive (α-synuclein BAC, LRRK2 KO) HD (tgHD)
rats, TgF344-AD) (APOE epsilon (PINK1 KO, DJ- (BACHD)
4 knock-in) 1 KO)
Molecular Mutation in APP, rRsk factors, Mainly loss-of- Mainly gain-of function, e.g., SNCA, CAG expansion CAG expansion
and PSEN1, e.g., APOE function, e.g., LRRK2 > 60 < 60
PARKIN, PINK1
hyperphosphorylation variants
biological of tau and DJ-1
basis
Strategy ● Expression/knock-in ● Humanization ● Knock out of ● Overexpression ● Overexpression ● Overexpression ● Overexpression
of a combination of of loci of AD PARKIN, PINK1 of wild-type or of wild-type or of full-length of the N-
multiple mutations in relevant or DJ-1 mutant SNCA mutant LRRK2 mutant HTT terminal
APP mutations ● KO fragment of
● Expression of mutant HTT
mutations in APP +
PSEN
● Expression of
mutations in MAPT
Pros ● Early and progressive ● Physiological ● Mitochondrial ● LB pathology ● Effect of impaired ● Early and ● Represents
recapitulation of levels of pathology can can be studied dopamine progressive the major form
neuropathological protein be studied homeostasis can be recapitulation of of HD
features expression studied the HTT ● Displays HD-
● Tangle-like ● Cranial aggregation like behavioral
pathology sensorimotor phenotype phenotypes
● Spatial cognition deficits can be ● Displays HD-
deficits studied (DJ-1 like behavioral
KO and PINK1 phenotypes
KO)
Cons ● Non-physiological ● Need to ● Most of ● No dopaminergic ● Represent only ● Mild and slow
condition verify and them do not neurodegeneration juvenile HD recapitulation of
● Represents a small characterize mimic the LB ● Long CAG disease
portion of disease form identified pathology of repeats may pathology
(early onset AD novel risk PD patients? change the HTT
accounts for < 5% of factors ● No motor protein
AD cases) behavior properties
impairment in
PARKIN KO
Literature Reviewed in [36-39] Reviewed Reviewed in [43-47] Reviewed in [48]
in [40-42]
AD: Alzheimer’s disease; APOE: apolipoprotein E; APP: amyloid precursor protein; CAG: polyglutamine; DJ-1 (PARK7): Parkinson’s disease protein
7; FAD: familial Alzheimer’s disease; FPD: familial Parkinson’s disease; HD: Huntington’s disease; HTT: huntingtin; KO: Knockout; LB: Lewy body;
LERRK2: leucine-rich repeat kinase 2; MAPT: microtubule-associated protein Tau; PINK1: PTEN-induced kinase 1; PSEN: presenilin; SNCA:
synuclein alpha.
review ). This raises the debate of whether the P301L resulting tau aggregation can represent tau pathology
[63]
in AD. Tau is a microtubule-associated protein stabilizing microtubules in the polymerized state [64,65] .
Alternative splicing of tau in humans generates six isoforms containing microtubule-binding domain,
including three (3R) or four (4R) microtubule-binding repeats . It has been shown that rats express all six
[66]
tau isoforms as humans, while mice only possess 3R tau isoforms .
[67]
The TgF344-AD rat is an AD transgenic model that carries transgenic constructs, expressing both the
Swedish human mutant APP and the PSEN1(PS1ΔE9). These rats exhibit 2.6-fold human APP and 6.2-fold
human presenilin-1 expression, respectively, compared to the endogenous rat homologs. Around 16
months of age, TgF344-AD rats develop amyloid plaques, some of which are thioflavin S-positive dense-
core plaques. Strikingly, abundant insoluble tau structures have also been demonstrated in the cortex and
hippocampus of aged transgenic animals, whose morphology recapitulates human NFTs. Frank and
progressive neurodegeneration combined with neuroinflammation and cell apoptosis have been found in
[68]
the same brain areas . Similarly, tangle-like tau aggregates were also observed in a wild-type rat injection