Page 30 - Read Online
P. 30
Brenac et al. Art Int Surg 2024;4:296-315 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ais.2024.49 Page 298
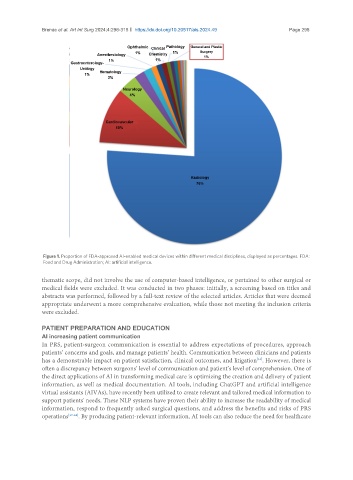
Figure 1. Proportion of FDA-approved AI-enabled medical devices within different medical disciplines, displayed as percentages. FDA:
Food and Drug Administration; AI: artificial intelligence.
thematic scope, did not involve the use of computer-based intelligence, or pertained to other surgical or
medical fields were excluded. It was conducted in two phases: initially, a screening based on titles and
abstracts was performed, followed by a full-text review of the selected articles. Articles that were deemed
appropriate underwent a more comprehensive evaluation, while those not meeting the inclusion criteria
were excluded.
PATIENT PREPARATION AND EDUCATION
AI increasing patient communication
In PRS, patient-surgeon communication is essential to address expectations of procedures, approach
patients’ concerns and goals, and manage patients’ health. Communication between clinicians and patients
has a demonstrable impact on patient satisfaction, clinical outcomes, and litigation . However, there is
[16]
often a discrepancy between surgeons’ level of communication and patient’s level of comprehension. One of
the direct applications of AI in transforming medical care is optimizing the creation and delivery of patient
information, as well as medical documentation. AI tools, including ChatGPT and artificial intelligence
virtual assistants (AIVAs), have recently been utilized to create relevant and tailored medical information to
support patients' needs. These NLP systems have proven their ability to increase the readability of medical
information, respond to frequently asked surgical questions, and address the benefits and risks of PRS
operations [17-24] . By producing patient-relevant information, AI tools can also reduce the need for healthcare