Page 89 - Read Online
P. 89
Wei et al. Art Int Surg 2024;4:187-98 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ais.2024.12 Page 195
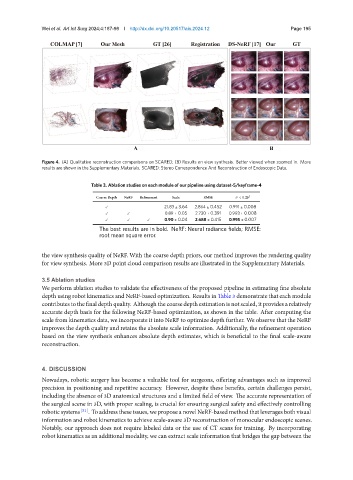
Figure 4. (A) Qualitative reconstruction comparisons on SCARED; (B) Results on view synthesis. Better viewed when zoomed in. More
results are shown in the Supplementary Materials. SCARED: Stereo Correspondence And Reconstruction of Endoscopic Data.
Table 3. Ablation studies on each module of our pipeline using dataset-5/keyframe-4
Coarse Depth NeRF Refinement Scale RMSE < 1.25 1
✓ 21.83 ± 3.64 2.864 ± 0.452 0.991 ± 0.008
✓ ✓ 0.89 ± 0.05 2.730 ± 0.391 0.993 ± 0.008
✓ ✓ ✓ 0.90 ± 0.04 2.688 ± 0.415 0.995 ± 0.007
The best results are in bold. NeRF: Neural radiance fields; RMSE:
root mean square error.
the view synthesis quality of NeRF. With the coarse depth priors, our method improves the rendering quality
for view synthesis. More 3D point cloud comparison results are illustrated in the Supplementary Materials.
3.5 Ablation studies
We perform ablation studies to validate the effectiveness of the proposed pipeline in estimating fine absolute
depth using robot kinematics and NeRF-based optimization. Results in Table 3 demonstrate that each module
contributestothefinaldepthquality. Although thecoarsedepthestimationisnotscaled, itprovidesarelatively
accurate depth basis for the following NeRF-based optimization, as shown in the table. After computing the
scale from kinematics data, we incorporate it into NeRF to optimize depth further. We observe that the NeRF
improves the depth quality and retains the absolute scale information. Additionally, the refinement operation
based on the view synthesis enhances absolute depth estimates, which is beneficial to the final scale-aware
reconstruction.
4. DISCUSSION
Nowadays, robotic surgery has become a valuable tool for surgeons, offering advantages such as improved
precision in positioning and repetitive accuracy. However, despite these benefits, certain challenges persist,
including the absence of 3D anatomical structures and a limited field of view. The accurate representation of
the surgical scene in 3D, with proper scaling, is crucial for ensuring surgical safety and effectively controlling
robotic systems [31] . To address these issues, we propose a novel NeRF-based method that leverages both visual
information and robot kinematics to achieve scale-aware 3D reconstruction of monocular endoscopic scenes.
Notably, our approach does not require labeled data or the use of CT scans for training. By incorporating
robot kinematics as an additional modality, we can extract scale information that bridges the gap between the