Page 88 - Read Online
P. 88
Page 194 Wei et al. Art Int Surg 2024;4:187-98 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ais.2024.12
Table 2. Quantitative comparisons for scale-aware depth estimation on SCARED
Error ↓ Accuracy ↑
Method Scale
Abs Rel Sq Rel RMSE RMSE log < 1.25 1 < 1.25 2
COLMAP [7] 4.04 ± 2.24 0.044 ± 0.028 0.391 ± 0.435 4.766 ± 2.506 0.065 ± 0.033 0.979 ± 0.036 0.998 ± 0.006
EndoSLAM [30] 77.77 ± 17.10 0.079 ± 0.047 0.897 ± 1.090 7.160 ± 4.818 0.099 ± 0.052 0.931 ± 0.124 0.997 ± 0.009
AF-SfMLearner [10] 2.12 ± 0.45 0.056 ± 0.028 0.437 ± 0.560 5.103 ± 3.143 0.073 ± 0.034 0.979 ± 0.047 0.999 ± 0.005
DS-NeRF [17] 22.04 ± 9.75 0.049 ± 0.034 0.458 ± 1.012 4.866 ± 3.432 0.070 ± 0.041 0.972 ± 0.067 0.997 ± 0.012
Ours 0.95 ± 0.07 0.048 ± 0.025 0.347 ± 0.351 4.583 ± 2.247 0.066 ± 0.030 0.984 ± 0.029 0.999 ± 0.003
The closer the scale is to 1, the better. The best result is in bold. The second best is underlined. SCARED: Stereo
Correspondence And Reconstruction of Endoscopic Data; RMSE: root mean square error; NeRF: neural radiance
fields.
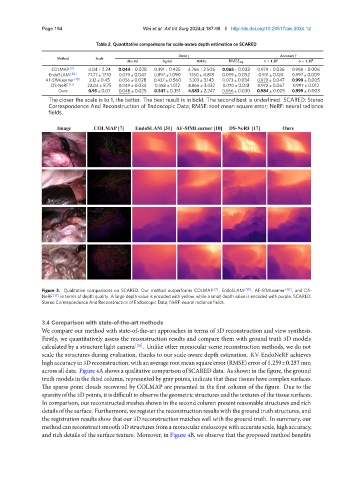
Figure 3. Qualitative comparisons on SCARED. Our method outperforms COLMAP [7] , EndoSLAM [30] , AF-SfMLearner [10] , and DS-
NeRF [17] in terms of depth quality. A large depth value is encoded with yellow, while a small depth value is encoded with purple. SCARED:
Stereo Correspondence And Reconstruction of Endoscopic Data; NeRF: neural radiance fields.
3.4 Comparison with state-of-the-art methods
We compare our method with state-of-the-art approaches in terms of 3D reconstruction and view synthesis.
Firstly, we quantitatively assess the reconstruction results and compare them with ground truth 3D models
calculated by a structure light camera [26] . Unlike other monocular scene reconstruction methods, we do not
scale the structures during evaluation, thanks to our scale-aware depth estimation. KV-EndoNeRF achieves
highaccuracyin3Dreconstruction, withanaveragerootmeansquareerror(RMSE)errorof 1.259±0.257mm
across all data. Figure 4A shows a qualitative comparison of SCARED data. As shown in the figure, the ground
truth models in the third column, represented by gray points, indicate that these tissues have complex surfaces.
The sparse point clouds recovered by COLMAP are presented in the first column of the figure. Due to the
sparsityofthe3Dpoints, itisdifficulttoobservethegeometricstructuresandthetexturesofthetissuesurfaces.
In comparison, our reconstructed meshes shown in the second column present reasonable structures and rich
detailsofthesurface. Furthermore, weregisterthereconstructionresultswiththegroundtruthstructures, and
the registration results show that our 3D reconstruction matches well with the ground truth. In summary, our
methodcanreconstructsmooth3Dstructuresfromamonocularendoscopewithaccuratescale, highaccuracy,
and rich details of the surface texture. Moreover, in Figure 4B, we observe that the proposed method benefits