Page 18 - Read Online
P. 18
Scherman. Rare Dis Orphan Drugs J 2023;2:12 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/rdodj.2023.01 Page 9 of 35
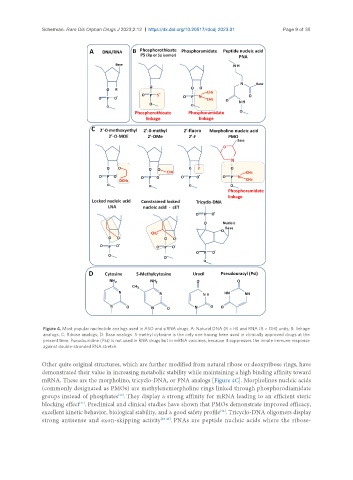
Figure 4. Most popular nucleotide analogs used in ASO and siRNA drugs. A: Natural DNA (R = H) and RNA (R = OH) units; B: linkage
analogs. C: Ribose analogs; D: Base analogs. 5-methyl cytosine is the only one having been used in clinically approved drugs at the
present time. Pseudouridine (Psi) is not used in RNA drugs but in mRNA vaccines, because it suppresses the innate immune response
against double-stranded RNA stretch.
Other quite original structures, which are further modified from natural ribose or deoxyribose rings, have
demonstrated their value in increasing metabolic stability while maintaining a high binding affinity toward
mRNA. These are the morpholino, tricyclo-DNA, or PNA analogs [Figure 4C]. Morpholinos nucleic acids
(commonly designated as PMOs) are methylenemorpholine rings linked through phosphorodiamidate
groups instead of phosphates . They display a strong affinity for mRNA leading to an efficient steric
[40]
blocking effect . Preclinical and clinical studies have shown that PMOs demonstrate improved efficacy,
[41]
excellent kinetic behavior, biological stability, and a good safety profile . Tricyclo-DNA oligomers display
[42]
strong antisense and exon-skipping activity [43-44] . PNAs are peptide nucleic acids where the ribose-