Page 66 - Read Online
P. 66
Xiao et al. Microstructures 2023;3:2023006 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/microstructures.2022.26 Page 7 of 17
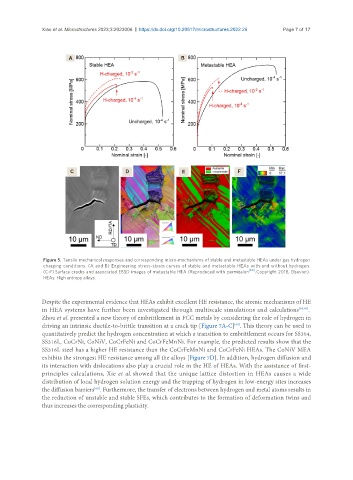
Figure 5. Tensile mechanical responses and corresponding micro-mechanisms of stable and metastable HEAs under gas hydrogen
charging conditions. (A and B) Engineering stress-strain curves of stable and metastable HEAs with and without hydrogen.
(C-F) Surface cracks and associated EBSD images of metastable HEA (Reproduced with permission [60] . Copyright 2018, Elsevier).
HEAs: High entropy alloys.
Despite the experimental evidence that HEAs exhibit excellent HE resistance, the atomic mechanisms of HE
in HEA systems have further been investigated through multiscale simulations and calculations [68,69] .
Zhou et al. presented a new theory of embrittlement in FCC metals by considering the role of hydrogen in
driving an intrinsic ductile-to-brittle transition at a crack tip [Figure 7A-C] . This theory can be used to
[68]
quantitatively predict the hydrogen concentration at which a transition to embrittlement occurs for SS304,
SS316L, CoCrNi, CoNiV, CoCrFeNi and CoCrFeMnNi. For example, the predicted results show that the
SS316L steel has a higher HE resistance than the CoCrFeMnNi and CoCrFeNi HEAs. The CoNiV MEA
exhibits the strongest HE resistance among all the alloys [Figure 7D]. In addition, hydrogen diffusion and
its interaction with dislocations also play a crucial role in the HE of HEAs. With the assistance of first-
principles calculations, Xie et al. showed that the unique lattice distortion in HEAs causes a wide
distribution of local hydrogen solution energy and the trapping of hydrogen in low-energy sites increases
the diffusion barriers . Furthermore, the transfer of electrons between hydrogen and metal atoms results in
[69]
the reduction of unstable and stable SFEs, which contributes to the formation of deformation twins and
thus increases the corresponding plasticity.