Page 481 - Read Online
P. 481
Page 6 of 9 Agdamag et al. Vessel Plus 2020;4:42 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2020.60
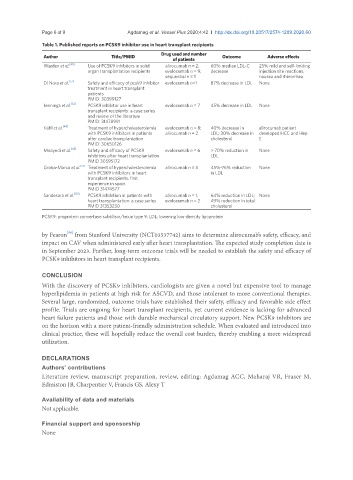
Table 1. Published reports on PCSK9 inhibitor use in heart transplant recipients
Author Title/PMID Drug used and number Outcome Adverse effects
of patients
Warden et al. [49] Use of PCSK9 inhibitors in solid alirocumab n = 2; 60% median LDL-C 25% mild and self-limiting
organ transplantation recipients evolocumab n = 9; decrease injection site reactions,
sequential n = 1 nausea and rhinorrhea
Di Nora et al. [57] Safety and efficacy of pcsk9 inhibitor evolocumab n=1 87% decrease in LDL None
treatment in heart transplant
patients
PMID: 30399127
Jennings et al. [52] PCSK9 inhibitor use in heart evolocumab n = 7 45% decrease in LDL None
transplant recipients: a case series
and review of the literature
PMID: 31478991
Kühl et al. [44] Treatment of hypercholesterolemia evolocumab n = 8; 40% decrease in alirocumab patient
with PCSK9 inhibitors in patients alirocumab n = 2 LDL; 30% decrease in developed HCC and Hep
after cardiac transplantation cholesterol E
PMID: 30650126
Moayedi et al. [45] Safety and efficacy of PCSK9 evolocumab n = 6 > 70% reduction in None
inhibitors after heart transplantation LDL
PMID 30595172
Groba-Marco et al. [51] Treatment of hypercholesterolemia alirocumab n = 5 45%-76% reduction None
with PCSK9 inhibitors in heart in LDL
transplant recipients. first
experience in spain.
PMID 31474577
Sandesara et al. [50] PCSK9 inhibition in patients with alirocumab n = 1; 64% reduction in LDL; None
heart transplantation: a case series evolocumab n = 2 49% reduction in total
PMID 31353230 cholesterol
PCSK9: proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9; LDL: lowering low-density lipoprotein
[56]
by Fearon from Stanford University (NCT03537742) aims to determine alirocumab’s safety, efficacy, and
impact on CAV when administered early after heart transplantation. The expected study completion date is
in September 2023. Further, long-term outcome trials will be needed to establish the safety and efficacy of
PCSK9 inhibitors in heart transplant recipients.
CONCLUSION
With the discovery of PCSK9 inhibitors, cardiologists are given a novel but expensive tool to manage
hyperlipidemia in patients at high risk for ASCVD, and those intolerant to more conventional therapies.
Several large, randomized, outcome trials have established their safety, efficacy and favorable side effect
profile. Trials are ongoing for heart transplant recipients, yet current evidence is lacking for advanced
heart failure patients and those with durable mechanical circulatory support. New PCSK9 inhibitors are
on the horizon with a more patient-friendly administration schedule. When evaluated and introduced into
clinical practice, these will hopefully reduce the overall cost burden, thereby enabling a more widespread
utilization.
DECLARATIONS
Authors’ contributions
Literature review, manuscript preparation, review, editing: Agdamag ACC, Maharaj VR, Fraser M,
Edmiston JB, Charpentier V, Francis GS, Alexy T
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Financial support and sponsorship
None