Page 440 - Read Online
P. 440
Ghoneim et al. Vessel Plus 2020;4:38 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2020.35 Page 3 of 9
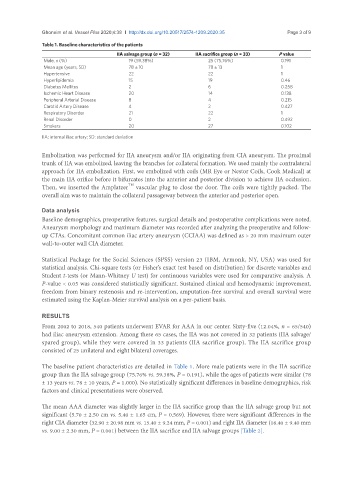
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of the patients
IIA salvage group (n = 32) IIA sacrifice group (n = 33) P value
Male, n (%) 19 (59.38%) 25 (75.76%) 0.191
Mean age (years, SD) 78 ± 10 78 ± 13 1
Hypertensive 22 22 1
Hyperlipidemia 15 19 0.46
Diabetes Mellitus 2 6 0.258
Ischemic Heart Disease 20 14 0.138
Peripheral Arterial Disease 8 4 0.215
Carotid Artery Disease 4 2 0.427
Respiratory Disorder 21 22 1
Renal Disorder 0 2 0.492
Smokers 20 27 0.102
IIA: internal iliac artery; SD: standard deviation
Embolization was performed for IIA aneurysm and/or IIA originating from CIA aneurysm. The proximal
trunk of IIA was embolized, leaving the branches for collateral formation. We used mainly the contralateral
approach for IIA embolization. First, we embolized with coils (MR Eye or Nestor Coils, Cook Medical) at
the main IIA orifice before it bifurcates into the anterior and posterior division to achieve IIA occlusion.
TM
Then, we inserted the Amplatzer vascular plug to close the door. The coils were tightly packed. The
overall aim was to maintain the collateral passageway between the anterior and posterior open.
Data analysis
Baseline demographics, preoperative features, surgical details and postoperative complications were noted.
Aneurysm morphology and maximum diameter was recorded after analyzing the preoperative and follow-
up CTAs. Concomitant common iliac artery aneurysm (CCIAA) was defined as > 20 mm maximum outer
wall-to-outer wall CIA diameter.
Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) version 23 (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA) was used for
statistical analysis. Chi-square tests (or Fisher’s exact test based on distribution) for discrete variables and
Student t-tests (or Mann-Whitney U test) for continuous variables were used for comparative analysis. A
P-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Sustained clinical and hemodynamic improvement,
freedom from binary restenosis and re-intervention, amputation-free survival and overall survival were
estimated using the Kaplan-Meier survival analysis on a per-patient basis.
RESULTS
From 2002 to 2018, 540 patients underwent EVAR for AAA in our center. Sixty-five (12.04%, n = 65/540)
had iliac aneurysm extension. Among these 65 cases, the IIA was not covered in 32 patients (IIA salvage/
spared group), while they were covered in 33 patients (IIA sacrifice group). The IIA sacrifice group
consisted of 25 unilateral and eight bilateral coverages.
The baseline patient characteristics are detailed in Table 1. More male patients were in the IIA sacrifice
group than the IIA salvage group (75.76% vs. 59.38%, P = 0.191), while the ages of patients were similar (78
± 13 years vs. 78 ± 10 years, P = 1.000). No statistically significant differences in baseline demographics, risk
factors and clinical presentations were observed.
The mean AAA diameter was slightly larger in the IIA sacrifice group than the IIA salvage group but not
significant (5.70 ± 2.50 cm vs. 5.40 ± 1.65 cm, P = 0.569). However, there were significant differences in the
right CIA diameter (32.90 ± 20.98 mm vs. 15.40 ± 9.24 mm, P = 0.001) and right IIA diameter (16.40 ± 9.40 mm
vs. 9.00 ± 2.30 mm, P = 0.001) between the IIA sacrifice and IIA salvage groups [Table 2].