Page 389 - Read Online
P. 389
Pisano et al. Vessel Plus 2020;4:33 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2020.21 Page 7 of 13
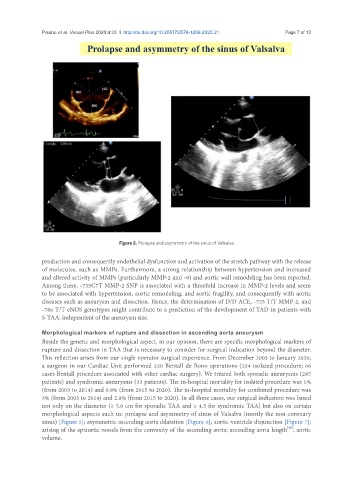
Figure 5. Prolapse and asymmetry of the sinus of Valsalva
production and consequently endothelial dysfunction and activation of the stretch pathway with the release
of molecules, such as MMPs. Furthermore, a strong relationship between hypertension and increased
and altered activity of MMPs (particularly MMP-2 and -9) and aortic wall remodeling has been reported.
Among these, -735C7T MMP-2 SNP is associated with a threefold increase in MMP-2 levels and seem
to be associated with hypertension, aortic remodeling, and aortic fragility, and consequently with aortic
diseases such as aneurysm and dissection. Hence, the determination of D/D ACE, -735 T/T MMP-2, and
-786 T/T eNOS genotypes might contribute to a prediction of the development of TAD in patients with
S-TAA, independent of the aneurysm size.
Morphological markers of rupture and dissection in ascending aorta aneurysm
Beside the genetic and morphological aspect, in our opinion, there are specific morphological markers of
rupture and dissection in TAA that is necessary to consider for surgical indication beyond the diameter.
This reflection arises from our single operator surgical experience. From December 2003 to January 2020,
a surgeon in our Cardiac Unit performed 320 Bentall de Bono operations (254 isolated procedure; 66
cases Bentall procedure associated with other cardiac surgery). We treated both sporadic aneurysms (287
patients) and syndromic aneurysms (33 patients). The in-hospital mortality for isolated procedure was 1%
(from 2003 to 2014) and 0.8% (from 2015 to 2020). The in-hospital mortality for combined procedure was
3% (from 2003 to 2014) and 2.8% (from 2015 to 2020). In all these cases, our surgical indication was based
not only on the diameter (≥ 5.0 cm for sporadic TAA and ≥ 4.5 for syndromic TAA) but also on certain
morphological aspects such us: prolapse and asymmetry of sinus of Valsalva (mostly the non-coronary
sinus) [Figure 5]; asymmetric ascending aorta dilatation [Figure 6]; aortic-ventricle disjunction [Figure 7];
[60]
arising of the epiaortic vessels from the convexity of the ascending aorta; ascending aorta length ; aortic
volume.