Page 30 - Read Online
P. 30
Page 4 of 10 Watanabe. Vessel Plus 2020;4:4 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2019.27
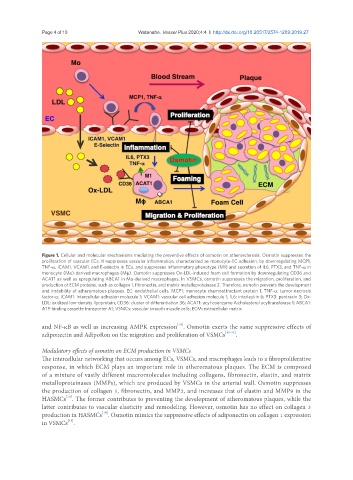
Figure 1. Cellular and molecular mechanisms mediating the preventive effects of osmotin on atherosclerosis. Osmotin suppresses the
proliferation of vascular ECs. It suppresses vascular inflammation, characterized as monocyte-EC adhesion, by downregulating MCP1,
TNF-α, ICAM1, VCAM1, and E-selectin in ECs, and suppresses inflammatory phenotype (M1) and secretion of IL6, PTX3, and TNF-α in
monocyte (Mo)-derived macrophages (Mφ). Osmotin suppresses Ox-LDL-induced foam cell formation by downregulating CD36 and
ACAT1 as well as upregulating ABCA1 in Mo-derived macrophages. In VSMCs, osmotin suppresses the migration, proliferation, and
production of ECM proteins, such as collagen 1, fibronectin, and matrix metalloproteinase 2. Therefore, osmotin prevents the development
and instability of atheromatous plaques. EC: endothelial cells; MCP1: monocyte chemoattractant protein 1; TNF-α: tumor necrosis
factor-α; ICAM1: intercellular adhesion molecule 1; VCAM1: vascular cell adhesion molecule 1; IL6: interleukin 6; PTX3: pentraxin 3; Ox-
LDL: oxidized low-density lipoprotein; CD36: cluster of differentiation 36; ACAT1: acyl-coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase 1; ABCA1:
ATP-binding cassette transporter A1; VSMCs: vascular smooth muscle cells; ECM: extracellular matrix
[10]
and NF-κB as well as increasing AMPK expression . Osmotin exerts the same suppressive effects of
adiponectin and AdipoRon on the migration and proliferation of VSMCs [42-44] .
Modulatory effects of osmotin on ECM production in VSMCs
The intercellular networking that occurs among ECs, VSMCs, and macrophages leads to a fibroproliferative
response, in which ECM plays an important role in atheromatous plaques. The ECM is composed
of a mixture of vastly different macromolecules including collagens, fibronectin, elastin, and matrix
metalloproteinases (MMPs), which are produced by VSMCs in the arterial wall. Osmotin suppresses
the production of collagen 1, fibronectin, and MMP2, and increases that of elastin and MMP9 in the
[10]
HASMCs . The former contributes to preventing the development of atheromatous plaques, while the
latter contributes to vascular elasticity and remodeling. However, osmotin has no effect on collagen 3
[10]
production in HASMCs . Osmotin mimics the suppressive effects of adiponectin on collagen 1 expression
in VSMCs .
[45]