Page 23 - Read Online
P. 23
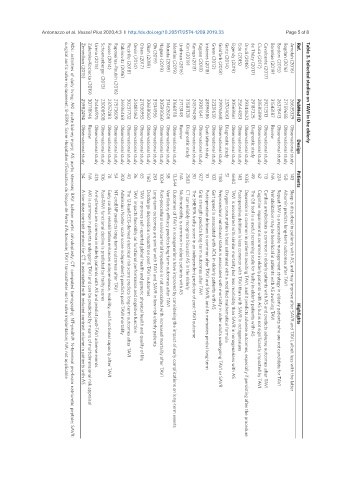
Antonazzo et al. Vessel Plus 2020;4:3 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2019.33 Page 5 of 8 Table 3. Selected studies on TAVI in the elderly
Ref.
Oh (2019)
Kim (2019)
Eide (2015)
Okoh (2019)
Drudi (2018)
Gertz (2014)
Ciuca (2017)
Olsen (2017)
Orvin (2014)
Urena (2015)
Russo (2014)
Green (2012)
Kamga (2013)
Kagase (2018)
Nagura (2019)
Bordoni (2015)
Bogdan (2016)
Murata (2019)
Elgendy (2019)
Mentias (2019)
Amofah (2016)
Piccirillo (2018)
Boreskie (2019)
Instenes (2018)
Lindman (2016)
Goldfarb (2018)
de Thézy (2017)
Rabinovitz (2016)
Zemedkun (2015)
Cavalcante (2017)
Schoenenberger (2013)
Zalenska-Kociecka (2019)
Raposeiras-Roubín (2016)
31668118
27113148
31587128
29212513
31514956
31543187
29301641
26378413
29187325
28396186
22331630
27159658
30569661
23757283
30718946
26635329
23704061
27573609
24579438
25644851
31462606
25466975
29976568
30237702
27036955
24481462
29344620
30618060
25982494
26936468
28585899
23008508
30599060
PubMed ID
Review
Review
Review
Design
Diagnostic study
Diagnostic study
Diagnostic study
Qualitative study
Observational study
Observational study
Observational study
Observational study
Observational study
Observational study
Observational study
Observational study
Observational study
Observational study
Observational study
Observational study
Observational study
Observational study
Observational study
Observational study
Observational study
Observational study
Observational study
Observational study
Observational study
Observational study
Observational study
Observational study
Observational study
Observational study
10
51
78
36
54
54
49
58
65
30
62
40
113
NA
NA
143
NA
143
261
102
150
106
302
224
927
435
1158
1160
1035
1004
2583
6680
13,544
Patients
Albumin predicts long-term outcomes after TAVI
CT can reliably recognize bicuspid AS in the elderly
NT-proBNP predicts long-term outcomes after TAVI
Multimorbidity is common in elderly patients with AS
Grip strength predicts long-term outcomes after TAVI
Discharge disposition impacts on post-TAVI outcomes
Post-TAVI functional decline is predicted by frailty scores
Ventilatory efficacy predicts long-term outcomes after TAVI
Gait speed is associated with ADL in elderly patients with AS
Prehabilitation may be beneficial in patients with AS awaiting TAVI
Highlights
TAVI impacts favorably on functional performance and cognitive function
Admission Norton scale score independently predicts post-TAVI mortality
The G8 tool is a useful screening scale for frailty in elderly patients with AS
The SHERPA frailty score in an independent predictor of post-TAVI outcome
Oxygen consumption is best estimated with a modified mathematical formula
Long-term outcomes are similar with TAVI and SAVR in low-risk elderly patients
Postoperative delirium is less common with TAVI than with SAVR in octogenarians
The 12-lead-ECG-derived electrical risk score predicts long-term outcomes after TAVI
TAVI improves self-reported global health and generic physical health and quality of life
Arrhythmias are common in elderly patients with AS and predict post-TAVI adverse events
Postoperative delirium is common after TAVI and SAVR, and its memories persist long-term
Post-procedural valvuloarterial impedance is not associated with increased mortality after TAVI
Early cardiac rehabilitation enhances independence, mobility, and functional capacity after TAVI
surgical aortic valve replacement; SHERPA: Score Hospitalier d’Evaluation du Risque de Perte d’Autonomie; TAVI: transcatheter aortic valve implantation; NA: not applicable
TAVI is associated with similar mortality but less morbidity than SAVR in nonagenarians with AS
A low-dose contrast protocol for CT is associated with reduced contrast volume in patients with AS
Repeat BAV is a reasonable management strategy in elderly patients who are not candidate for TAVI
Preprocedural nutritional status is associated with mortality in older adults undergoing TAVI or SAVR
Cognitive impairment is common in elderly patients with AS but is not significantly impacted by TAVI
Cardiac amyloidosis is common in elderly patients with AS and predicts adverse outcomes after TAVI
Sleep is disturbed in patients with AS, and may improve after SAVR and TAVI, albeit less with the latter
AKI is common in patients undergoing TAVI and can be predicted by means of multidimensional risk appraisal
Outcomes of TAVI in nonagenarians have improved by considering the impact of early complications on long-term events
Depression is common in patients awaiting TAVI, and it predicts adverse outcomes, especially if persisting after the procedure
ADL: activities of daily living; AKI: acute kidney injury; AS: aortic stenosis; BAV: balloon aortic valvuloplasty; CT: computed tomography; NT-proBNP: N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide; SAVR: