Page 217 - Read Online
P. 217
Page 4 of 11 Raja. Vessel Plus 2019;3:23 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2019.05
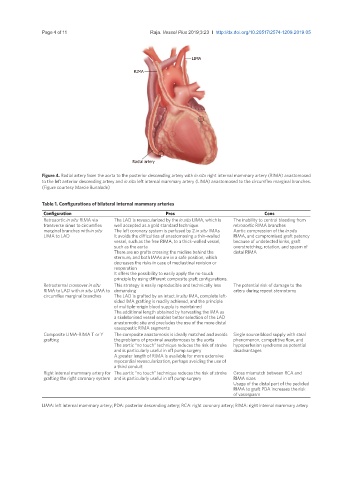
LIMA
RIMA
Radial artery
Figure 4. Radial artery from the aorta to the posterior descending artery with in situ right internal mammary artery (RIMA) anastomosed
to the left anterior descending artery and in situ left internal mammary artery (LIMA) anastomosed to the circumflex marginal branches.
(Figure courtesy Marcie Bunalade)
Table 1. Configurations of bilateral internal mammary arteries
Configuration Pros Cons
Retroaortic in situ RIMA via The LAD is revascularized by the in situ LIMA, which is The inability to control bleeding from
transverse sinus to circumflex well accepted as a gold standard technique retroaortic RIMA branches
marginal branches with in situ The left coronary system is perfused by 2 in situ IMAs Aortic compression of the in situ
LIMA to LAD It avoids the difficulties of anastomosing a thin-walled RIMA, and compromised graft patency
vessel, such as the free RIMA, to a thick-walled vessel, because of undetected kinks, graft
such as the aorta overstretching, rotation, and spasm of
There are no grafts crossing the midline behind the distal RIMA
sternum, and both IMAs are in a safe position, which
decreases the risks in case of mediastinal revision or
reoperation
It offers the possibility to easily apply the no-touch
principle by using different composite graft configurations.
Retrosternal crossover in situ This strategy is easily reproducible and technically less The potential risk of damage to the
RIMA to LAD with in situ LIMA to demanding artery during repeat sternotomy
circumflex marginal branches The LAD is grafted by an intact in situ IMA, complete left-
sided IMA grafting is readily achieved, and the principle
of multiple-origin blood supply is maintained
The additional length obtained by harvesting the IMA as
a skeletonised vessel enables better selection of the LAD
anastomotic site and precludes the use of the more distal
vasospastic RIMA segments
Composite LIMA-RIMA T or Y The composite anastomosis is ideally matched and avoids Single source blood supply with steal
grafting the problems of proximal anastomoses to the aorta phenomenon, competitive flow, and
The aortic “no touch” technique reduces the risk of stroke hypoperfusion syndrome as potential
and is particularly useful in off pump surgery disadvantages
A greater length of RIMA is available for more extensive
myocardial revascularization, perhaps avoiding the use of
a third conduit
Right internal mammary artery for The aortic “no touch” technique reduces the risk of stroke Gross mismatch between RCA and
grafting the right coronary system and is particularly useful in off pump surgery RIMA sizes
Usage of the distal part of the pedicled
RIMA to graft PDA increases the risk
of vasospasm
LIMA: left internal mammary artery; PDA: posterior descending artery; RCA: right coronary artery; RIMA: right internal mammary artery