Page 208 - Read Online
P. 208
Page 4 of 9 Pragliola et al. Vessel Plus 2019;3:22 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2019.003
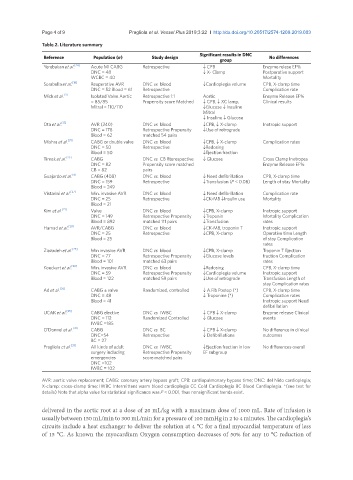
Table 2. Literature summary
Significant results in DNC
Reference Population (n) Study design No differences
group
Yerebakan et al. [24] Acute MI CABG Retrospective ↓ CPB Enzyme relese EF%
DNC = 48 ↓ X- Clamp Postperative support
WCBC = 40 Mortality
Sorabella et al. [18] Reoperative AVR DNC vs. blood ↓Cardioplegia volume CPB, X-clamp time
DNC = 52 Blood = 61 Retrospective Complication rate
Mick et al. [3] Isolated Valve Aortic Retrospective 1:1 Aortic Ensyme Release EF%
= 85/85 Propensity score Matched ↓ CPB, ↓ XC lamp, Clinical results
Mitral = 110/110 ↓Glucose ↓ Insuline
Mitral
↓ Insuline ↓ Glucose
Ota et al. [17] AVR (240) DNC vs. blood ↓CPB, ↓ X-clamp Inotropic support
DNC = 178 Retrospective Propensity ↓Use of retrograde
Blood = 62 matched 54 pairs
Mishra et al. [31] CABG or double valve DNC vs. blood ↓CPB, ↓ X-clamp Complication rates
DNC = 50 Retrospective ↓Redosing
Blood = 50 ↓Ejection fraction
Timek et al. [23] CABG DNC vs. CB Rterospective ↓ Glucose Cross Clamp Inotropes
DNC = 82 Propensity score matched Enzyme Release EF%
CB = 82 pairs
Guajardo et al. [4] CABG (408) DNC vs. blood ↓ Need defibrillation CPB, X-clamp time
DNC = 159 Retrospective ↓Transfusion (P < 0.08) Length of stay Mortality
Blood = 249
Vistarini et al. [27] Min. invasive AVR DNC vs. blood ↓ Need defibrillation Complication rate
DNC = 25 Retrospective ↓CK-MB ↓Insulin use Mortality
Blood = 21
Kim et al. [21] Valve DNC vs. blood ↓CPB, X-clamp Inotropic support
DNC = 149 Retrospective Propensity ↓Troponin Mortality Complication
Blood = 892 matched 111 pairs ↓Transfusion rates
Hamad et al. [28] AVR/CABG DNC vs. blood ↓CK-MB, troponin T Inotropic support
DNC = 25 Retrospective ↓CPB, X-clamp Operative time Length
Blood = 25 of stay Complication
rates
Ziazadeh et al. [29] Min invasive AVR DNC vs. blood ↓CPB, X-clamp Troponin T Ejection
DNC = 77 Retrospective Propensity ↓Glucose levels fraction Complication
Blood = 101 matched 63 pairs rates
Koeckert et al. [30] Min. invasive AVR DNC vs. blood ↓Redosing CPB, X-clamp time
DNC = 59 Retrospective Propensity ↓Cardioplegia volume Inotropic support
Blood = 122 matched 59 pairs ↓Use of retrograde Transfusion Length of
stay Complication rates
Ad et al. [26] CABG ± valve Randomized, controlled ↓ A.Fib Postop (*) CPB, X-clamp time
DNC = 48 ↓ Troponine (*) Complication rates
Blood = 41 Inotropic support Need
defibrillation
UCAK et al. [25] CABG elective DNC vs. IWBC ↓ CPB ↓ X-clamp Enzyme release Clinical
DNC = 112 Randomized Controlled ↓ Glucose events
IWBC =185
O’Donnel et al. [20] CABG DNC vs. BC ↓ CPB ↓ X-clamp No difference in clinical
DNC=54 Retrospective ↓ Defibrillations outcomes
BC = 27
Pragliola et al. [33] All kinds of adult DNC vs. IWBC ↓Ejection fraction in low No differences overall
surgery including Retrospective Propensity EF subgroup
emergencies score matched pairs
DNC =102
IWBC = 102
AVR: aortic valve replacement; CABG: coronary artery bypass graft; CPB: cardiopulmonary bypass time; DNC: del Nido cardioplegia;
X-clamp: cross-clamp time; IWBC Intermittent warm blood cardioplegia CC Cold Cardioplegia BC Blood Cardioplegia. *(see text for
details) Note that alpha value for statistical significance was P < 0.001, thus nonsignificant trends exist.
delivered in the aortic root at a dose of 20 mL/kg with a maximum dose of 1000 mL. Rate of infusion is
usually between 150 mL/min to 300 mL/min for a pressure of 100 mmHg in 2 to 4 minutes. The cardioplegia’s
circuits include a heat exchanger to deliver the solution at 4 °C for a final myocardial temperature of less
of 15 °C. As known the myocardium Oxygen consumption decreases of 50% for any 10 °C reduction of