Page 276 - Read Online
P. 276
Strassheim et al. Vessel Plus 2018;2:29 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2018.44 Page 7 of 22
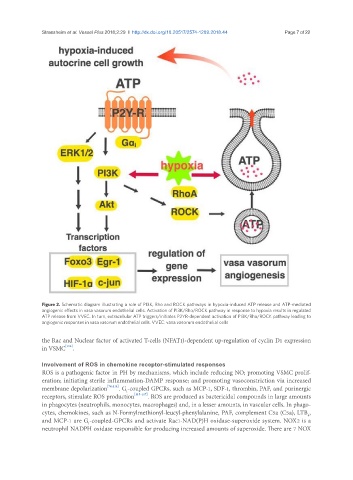
Figure 2. Schematic diagram illustrating a role of PI3K, Rho and ROCK pathways in hypoxia-induced ATP release and ATP-mediated
angiogenic effects in vasa vasorum endothelial cells. Activation of PI3K/Rho/ROCK pathway in response to hypoxia results in regulated
ATP release from VVEC. In turn, extracellular ATP triggers/initiates P2YR-dependent activation of PI3K/Rho/ROCK pathway leading to
angiogenic responses in vasa vasorum endothelial cells. VVEC: vasa vasorum endothelial cells
the Rac and Nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT1)-dependent up-regulation of cyclin D1 expression
[113]
in VSMC .
Involvement of ROS in chemokine receptor-stimulated responses
ROS is a pathogenic factor in PH by mechanisms, which include reducing NO; promoting VSMC prolif-
eration; initiating sterile inflammation-DAMP response; and promoting vasoconstriction via increased
membrane depolarization [74,114] . G-coupled GPCRs, such as MCP-1, SDF-1, thrombin, PAF, and purinergic
i
receptors, stimulate ROS production [115-117] . ROS are produced as bactericidal compounds in large amounts
in phagocytes (neutrophils, monocytes, macrophages) and, in a lesser amounts, in vascular cells. In phago-
cytes, chemokines, such as N-Formylmethionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine, PAF, complement C5a (C5a), LTB ,
4
and MCP-1 are G-coupled-GPCRs and activate Rac1-NAD(P)H oxidase-superoxide system. NOX2 is a
i
neutrophil NADPH oxidase responsible for producing increased amounts of superoxide. There are 7 NOX