Page 273 - Read Online
P. 273
Page 4 of 22 Strassheim et al. Vessel Plus 2018;2:29 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2018.44
Table 2. Current G protein-coupled receptor clinical trials in pulmonary hypertension
Clinical trials name Sponsor Drug Target
Tomorrow Acetilon Macitentan ET A /ET B
antagonist
ADAPT United therapeutics IP agonist
Orenitram IP agonist
Lung biotechnology BPS-314d oral treprostanil IP agonist
Arena pharmaceuticals APD-811 IP agonist
INSPIRE Liquidia technologies Inhaled treprostanil IP agonist
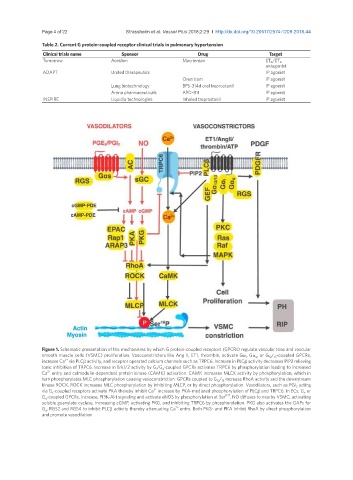
Figure 1. Schematic presentation of the mechanisms by which G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) regulate vascular tone and vascular
smooth muscle cells (VSMC) proliferation. Vasoconstrictors like Ang II, ET1, thrombin, activate Ga i , Ga q , or G 12 / 13 -coupled GPCRs,
2+
increase Ca via PLCb activity, and receptor operated calcium channels such as TRPC6. Increase in PLCb activity decreases PIP2 relieving
tonic inhibition of TRPC6. Increase in Erk1/2 activity by G i /G q -coupled GPCRs activates TRPC6 by phosphorylation leading to increased
2+
Ca entry and calmodulin-dependent protein kinase (CAMK) activation. CAMK increases MLCK activity by phosphorylation, which in
turn phosphorylates MLC phosphorylation causing vasoconstriction. GPCRs coupled to G 12 / 13 increase RhoA activity and the downstream
kinase ROCK. ROCK increases MLC phosphorylation by inhibiting MLCP, or by direct phosphorylation. Vasodilators, such as PGI 2 acting
2+
via G s -coupled receptors activate PKA thereby inhibit Ca increase by PKA-mediated phosphorylation of PLCb and TRPC6. In ECs, G i , or
1177
G q -coupled GPCRs, increase, PI3K-Akt signaling and activate eNOS by phosphorylation at Ser . NO diffuses to nearby VSMC, activating
soluble guanylate cyclase, increasing cGMP, activating PKG, and inhibiting TRPC6 by phosphorylation. PKG also activates the GAPs for
2+
G q , RGS2 and RGS4 to inhibit PLCb activity thereby attenuating Ca entry. Both PKG- and PKA inhibit RhoA by direct phosphorylation
and promote vasodilation