Page 207 - Read Online
P. 207
Saxena et al. Vessel Plus 2022;6:15 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2021.96 Page 7 of 17
event rate
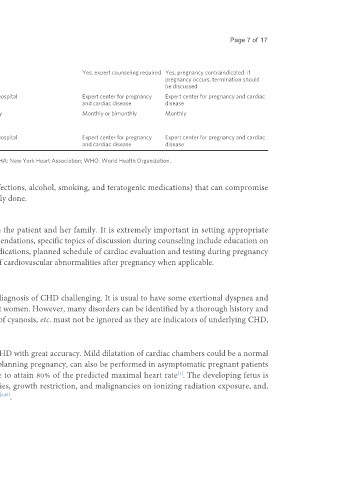
Counseling Yes Yes Yes Yes, expert counseling required Yes, pregnancy contraindicated: if
pregnancy occurs, termination should
be discussed
Care during Local hospital Local hospital Referral hospital Expert center for pregnancy Expert center for pregnancy and cardiac
pregnancy and cardiac disease disease
Minimal follow-up Once or twice Once per trimester Bimonthly Monthly or bimonthly Monthly
visits during
pregnancy
Location of delivery Local hospital Local hospital Referral hospital Expert center for pregnancy Expert center for pregnancy and cardiac
and cardiac disease disease
ASI: Aortic size index; EF: ejection fraction; mWHO: modified World Health Organization classification; NYHA: New York Heart Association; WHO: World Health Organization.
Assessment for other risk factors (parental obesity, diabetes, hypertension, infections, alcohol, smoking, and teratogenic medications) that can compromise
fetal well-being and increase the risk of fetal birth defects should also be routinely done.
Preconception counseling
A multidisciplinary management plan should be devised and discussed with the patient and her family. It is extremely important in setting appropriate
expectations and minimizing complications. In addition to the general recommendations, specific topics of discussion during counseling include education on
maternal and fetal risks, pre-pregnancy optimization plan, modification of medications, planned schedule of cardiac evaluation and testing during pregnancy
and in the peripartum time period, mode of delivery, and possible persistence of cardiovascular abnormalities after pregnancy when applicable.
DIAGNOSIS OF CHD DURING PREGNANCY
The physiological adaptations occurring during pregnancy make the clinical diagnosis of CHD challenging. It is usual to have some exertional dyspnea and
fatigue during pregnancy. Edema of feet can be seen in 80% of healthy pregnant women. However, many disorders can be identified by a thorough history and
physical examination. Unexplained dyspnea, pathological murmurs, presence of cyanosis, etc. must not be ignored as they are indicators of underlying CHD,
and an echocardiography is indicated in these cases .
[1]
Echocardiography is a widely available imaging tool which gives diagnosis of CHD with great accuracy. Mild dilatation of cardiac chambers could be a normal
finding during pregnancy. An exercise test, although best performed prior to planning pregnancy, can also be performed in asymptomatic pregnant patients
with underlying CHD. It is recommended to perform a submaximal exercise to attain 80% of the predicted maximal heart rate . The developing fetus is
[1]
vulnerable (highest during first trimester) to develop neurological abnormalities, growth restriction, and malignancies on ionizing radiation exposure, and,
hence, chest radiograph and computed tomography must be avoided if possible [1,35] .