Page 15 - Read Online
P. 15
Page 8 of 15 Tummala et al. Vessel Plus 2022;6:17 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2021.114
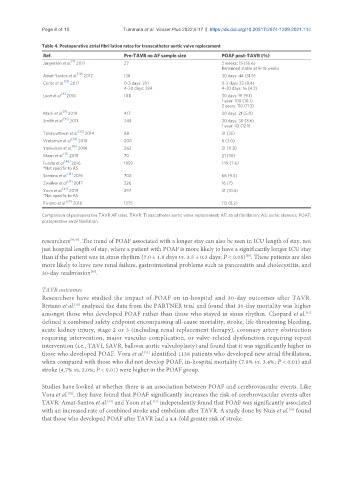
Table 4. Postoperative atrial fibrillation rates for transcatheter aortic valve replacement
Ref. Pre-TAVR no AF sample size POAF post-TAVR (%)
[7]
Jørgensen et al. 2017 27 2 weeks: 15 (55.6)
Remained stable at 8-10 weeks
[29]
Amat-Santos et al. 2012 138 30 days: 44 (31.9)
[33]
Conte et al. 2017 0-3 days: 391 0-3 days 33 (8.4)
4-30 days: 384 4-30 days: 16 (4.2)
[8]
Leon et al. 2016 1011 30 days: 91 (9.1)
1 year: 100 (10.1)
2 years: 110 (11.3)
[9]
Mack et al. 2019 417 30 days: 21 (5.0)
Smith et al. [10] 2011 348 30 days: 30 (8.6)
1 year: 42 (12.1)
Tanawuttiwat et al. [32] 2014 88 31 (35)
[34]
Waksman et al. 2018 200 6 (3.0)
[16]
Yankelson et al. 2014 262 31 (11.8)
[17]
Maan et al. 2015 70 21 (30)
[46]
Furuta et al. 2016 1959 149 (7.6)
*Not specific to AS
[18]
Sannino et al. 2016 708 66 (9.3)
Zweiker et al. [19] 2017 226 16 (7)
[47]
Yoon et al. 2019 297 31 (10.4)
*Not specific to AS
[20]
Biviano et al. 2016 1375 113 (8.2)
Comparison of postoperative TAVR AF rates. TAVR: Transcatheter aortic valve replacement; AF: atrial fibrillation; AS: aortic stenosis; POAF:
postoperative atrial fibrillation.
researchers [39,43] . The trend of POAF associated with a longer stay can also be seen in ICU length of stay, not
just hospital length of stay, where a patient with POAF is more likely to have a significantly longer ICU stay
[50]
than if the patient was in sinus rhythm (7.0 ± 1.8 days vs. 3.5 ± 0.3 days; P < 0.05) . These patients are also
more likely to have new renal failure, gastrointestinal problems such as pancreatitis and cholecystitis, and
[39]
30-day readmission .
TAVR outcomes
Researchers have studied the impact of POAF on in-hospital and 30-day outcomes after TAVR.
Biviano et al. analyzed the data from the PARTNER trial and found that 30-day mortality was higher
[20]
amongst those who developed POAF rather than those who stayed in sinus rhythm. Chopard et al.
[51]
defined a combined safety endpoint encompassing all-cause mortality, stroke, life-threatening bleeding,
acute kidney injury, stage 2 or 3 (including renal replacement therapy), coronary artery obstruction
requiring intervention, major vascular complication, or valve-related dysfunction requiring repeat
intervention (i.e., TAVI, SAVR, balloon aortic valvuloplasty) and found that it was significantly higher in
those who developed POAF. Vora et al. identified 1138 patients who developed new atrial fibrillation,
[52]
when compared with those who did not develop POAF, in-hospital mortality (7.8% vs. 3.4%; P < 0.01) and
stroke (4.7% vs. 2.0%; P < 0.01) were higher in the POAF group.
Studies have looked at whether there is an association between POAF and cerebrovascular events. Like
Vora et al. , they have found that POAF significantly increases the risk of cerebrovascular events after
[52]
TAVR. Amat-Santos et al. and Yoon et al. independently found that POAF was significantly associated
[29]
[47]
with an increased rate of combined stroke and embolism after TAVR. A study done by Nuis et al. found
[53]
that those who developed POAF after TAVR had a 4.4-fold greater risk of stroke.