Page 126 - Read Online
P. 126
Kuruvilla et al. Vessel Plus 2022;6:45 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2021.122 Page 5 of 9
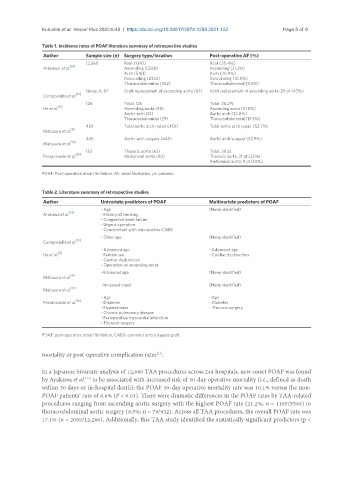
Table 1. Incidence rates of POAF literature summary of retrospective studies
Author Sample size (n) Surgery type/location Post-operative AF (%)
12,260 Root (1347) Root (20.4%)
[14]
Arakawa et al. Ascending (5588) Ascending (21.2%)
Arch (5161) Arch (20.9%)
Descending (2332) Descending (10.5%)
Thoracoabdominal (932) Thoracoabdominal (8.5%)
Group A: 67 Graft replacement of ascending aorta (67) Graft replacement of ascending aorta: 29 pt (43%)
Compostella et al. [15]
126 Total: 126 Total: 26.2%
[11]
He et al. Ascending aorta (88) Ascending aorta (31.8%)
Aortic arch (61) Aortic arch (32.8%)
Thoracoabdominal (29) Thoracoabdominal (13.8%)
459 Total aortic arch repair (459) Total aortic arch repair (52.7%)
[9]
Matsuura et al.
445 Aortic arch surgery (445) Aortic arch surgery (53.9%)
[12]
Matsuura et al.
153 Thoracic aorta (63) Total: 30 pt
Perzanowski et al. [16] Abdominal aorta (90) Thoracic aorta: 21 pt (33%)
Abdominal aorta: 9 pt (10%)
POAF: Post-operative atrial fibrillation; AF: atrial fibrillation; pt: patients.
Table 2. Literature summary of retrospective studies
Author Univariate predictors of POAF Multivariate predictors of POAF
- Age (None identified)
[14]
Arakawa et al. - History of smoking
- Congestive heart failure
- Urgent operation
- Concomitant with non-elective CABG
- Older age (None identified)
[15]
Compostella et al.
- Advanced age - Advanced age
[11]
He et al. - Female sex - Cardiac dysfunction
- Cardiac dysfunction
- Operation on ascending aorta
-Advanced age (None identified)
[9]
Matsuura et al.
-Increased input (None identified)
[12]
Matsuura et al.
- Age - Age
Perzanowski et al. [16] - Diabetes - Diabetes
- Hypertension - Thoracic surgery
- Chronic pulmonary disease
- Perioperative myocardial infarction
- Thoracic surgery
POAF: post-operative atrial fibrillation; CABG: coronary artery bypass graft.
mortality or post-operative complication rates .
[11]
In a Japanese bivariate analysis of 12,660 TAA procedures across 244 hospitals, new-onset POAF was found
by Arakawa et al. to be associated with increased risk of 30-day operative mortality (i.e., defined as death
[14]
within 30 days or in-hospital death); the POAF 30-day operative mortality rate was 10.1% versus the non-
POAF patients’ rate of 6.6% (P < 0.01). There were dramatic differences in the POAF rates by TAA-related
procedures ranging from ascending aortic surgery with the highest POAF rate (21.2%; n = 1185/5588) to
thoracoabdominal aortic surgery (8.5%; n = 79/932). Across all TAA procedures, the overall POAF rate was
17.1% (n = 2095/12,260). Additionally, this TAA study identified the statistically significant predictors (p <