Page 114 - Read Online
P. 114
Obeid et al. Vessel Plus 2022;6:43 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2021.136 Page 7 of 14
X*Significant association has been ventricular arrhythmias and mortality; *AF evaluated, not significant univariate predictor; **AF evaluated in
MV or Cox proportional hazards model, not a significant predictor; AF: atrial fibrillation; POAF: postoperative atrial fibrillation; LVAD: left
ventricular assist device; CABG: coronary artery bypass graft.
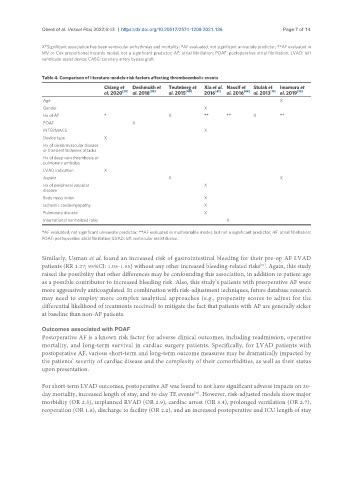
Table 4. Comparison of literature models-risk factors affecting thromboembolic events
Chiang et Deshmukh et Teuteberg et Xia et al. Nassif et Stulak et Imamura et
al. 2020 [20] al. 2018 [30] al. 2015 [40] 2016 [41] al. 2016 [44] al. 2013 [15] al. 2019 [33]
Age X
Gender X
Hx of AF * X ** ** X **
POAF X
INTERMACS X
Device type X
Hx of cerebrovascular disease
or transient Ischemic attacks
Hx of deep vein thrombosis or
pulmonary embolus
LVAD indication X
Aspirin X X
Hx of peripheral vascular X
disease
Body mass index X
Ischemic cardiomyopathy X
Pulmonary disease X
International normalized ratio X
*AF evaluated, not significant univariate predictor; **AF evaluated in multivariable model, but not a significant predictor; AF: atrial fibrillation;
POAF: postoperative atrial fibrillation; LVAD: left ventricular assist device.
Similarly, Usman et al. found an increased risk of gastrointestinal bleeding for their pre-op AF LVAD
patients (RR 1.27; 95%CI: 1.05-1.55) without any other increased bleeding-related risks . Again, this study
[51]
raised the possibility that other differences may be confounding this association, in addition to patient age
as a possible contributor to increased bleeding risk. Also, this study’s patients with preoperative AF were
more aggressively anticoagulated. In combination with risk-adjustment techniques, future database research
may need to employ more complex analytical approaches (e.g., propensity scores to adjust for the
differential likelihood of treatments received) to mitigate the fact that patients with AF are generally sicker
at baseline than non-AF patients.
Outcomes associated with POAF
Postoperative AF is a known risk factor for adverse clinical outcomes, including readmission, operative
mortality, and long-term survival in cardiac surgery patients. Specifically, for LVAD patients with
postoperative AF, various short-term and long-term outcome measures may be dramatically impacted by
the patients’ severity of cardiac disease and the complexity of their comorbidities, as well as their status
upon presentation.
For short-term LVAD outcomes, postoperative AF was found to not have significant adverse impacts on 30-
day mortality, increased length of stay, and 30-day TE events . However, risk-adjusted models show major
[30]
morbidity (OR 2.5), unplanned RVAD (OR 2.9), cardiac arrest (OR 3.4), prolonged ventilation (OR 2.7),
reoperation (OR 1.8), discharge to facility (OR 2.2), and an increased postoperative and ICU length of stay