Page 117 - Read Online
P. 117
Page 4 of 11 Scirpa et al. Vessel Plus 2022;6:52 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2021.74
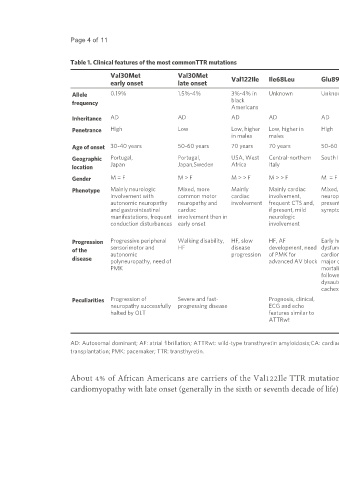
Table 1. Clinical features of the most commonTTR mutations
Val30Met Val30Met
early onset late onset Val122Ile Ile68Leu Glu89Gln Phe64Leu Thr60Ala Leu111Met Ile107Val
Allele 0.19% 1.5%-4% 3%-4% in Unknown Unknown Unknown 1% Unknown Unknown
frequency black
Americans
Inheritance AD AD AD AD AD AD AD AD AD
Penetrance High Low Low, higher Low, higher in High Medium Low High Unknown
in males males
Age of onset 30-40 years 50-60 years 70 years 70 years 50-60 years 65-70 years 50-60 years 30-40 years 65 years
Geographic Portugal, Portugal, USA, West Central-northern South Italy, Bulgaria South Italy North-west Denmark France
location Japan Japan,Sweden Africa Italy Ireland, UK
Gender M = F M > F M > > F M > > F M = F M > F M > > F M = F M > > F
Phenotype Mainly neurologic Mixed, more Mainly Mainly cardiac Mixed, usually Mixed, with earlier Predominantly Exclusive Mainly peripheric neurologic
involvement with common motor cardiac involvement, neuropathy as periphericthan cardiac and cardiac involvement, upper limb
autonomic neuropathy neuropathy and involvement frequent CTS and, presenting autonomic autonomic involvement weakness and gait disorders
and gastrointestinal cardiac if present, mild symptom neurologic involvement, < 1/4
manifestations, frequent involvement then in neurologic involvement patients with
conduction disturbances early onset involvement peripheral
neuropathy
Progression Progressive peripheral Walking disability, HF, slow HF, AF Early heart Severe peripheral HF, AF, need of HF Rapid onset of gait
of the sensorimotor and HF disease development, need dysfunction, neuropathy, death PMK, progression of disturbances,tetraparesis,
disease autonomic progression of PMK for cardiomyopathy as for wasting neuropathy. Poor short median survival.
polyneuropathy, need of advanced AV block major cause of syndrome prognosis
PMK mortality
followed by
dysautonomia and
cachexia
Peculiarities Progression of Severe and fast- Prognosis, clinical, Low sensitivity of Disease progression High penetrance Most debilitating and
neuropathy successfully progressing disease ECG and echo bone scintigraphy not modified by OLT and early onset severe neuropathy ever
halted by OLT features similar to to detect CA in contrast to described
ATTRwt other cardiac
mutations
AD: Autosomal dominant; AF: atrial fibrillation; ATTRwt: wild-type transthyretin amyloidosis;CA: cardiac amyloidosis; CTS: carpal tunnel syndrome; F: females; HF: heart failure; M: males; OLT: orthotopic liver
transplantation; PMK: pacemaker; TTR: transthyretin.
About 4% of African Americans are carriers of the Val122Ile TTR mutation. The predominant phenotypic feature of this mutation is severe restrictive
[17]
cardiomyopathy with late onset (generally in the sixth or seventh decade of life) without neurologic involvement .