Page 59 - Read Online
P. 59
Gonzaga-Jauregui et al. Rare Dis Orphan Drugs J 2024;3:16 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/rdodj.2024.02 Page 3 of 10
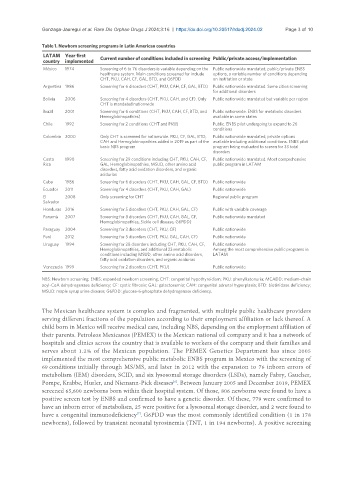
Table 1. Newborn screening programs in Latin American countries
LATAM Year first Current number of conditions included in screening Public/private access/implementation
country implemented
México 1974 Screening of 6 to 76 disorders is variable depending on the Public nationwide mandated; public/private ENBS
healthcare system. Main conditions screened for include options, a variable number of conditions depending
CHT, PKU, CAH, CF, GAL, BTD, and G6PDD on institution or state
Argentina 1986 Screening for 6 disorders (CHT, PKU, CAH, CF, GAL, BTD) Public nationwide mandated. Some cities screening
for additional disorders
Bolivia 2006 Screening for 4 disorders (CHT, PKU, CAH, and CF). Only Public nationwide mandated but variable per region
CHT is mandated nationwide
Brazil 2001 Screening for 6 conditions (CHT, PKU, CAH, CF, BTD, and Public nationwide. ENBS for metabolic disorders
Hemoglobinopathies) available in some states
Chile 1992 Screening for 2 conditions (CHT and PKU) Public. ENBS pilot undergoing to expand to 26
conditions
Colombia 2000 Only CHT is screened for nationwide. PKU, CF, GAL, BTD, Public nationwide mandated; private options
CAH and Hemoglobinopathies added in 2019 as part of the available including additional conditions. ENBS pilot
basic NBS program program being evaluated to screen for 33 total
disorders
Costa 1990 Screening for 29 conditions including CHT, PKU, CAH, CF, Public nationwide mandated. Most comprehensive
Rica GAL, Hemoglobinopathies, MSUD, other amino acid public program in LATAM
disorders, fatty acid oxidation disorders, and organic
acidurias
Cuba 1986 Screening for 6 disorders (CHT, PKU, CAH, GAL, CF, BTD) Public nationwide
Ecuador 2011 Screening for 4 disorders (CHT, PKU, CAH, GAL) Public nationwide
El 2008 Only screening for CHT Regional public program
Salvador
Honduras 2016 Screening for 5 disorders (CHT, PKU, CAH, GAL, CF) Public with variable coverage
Panamá 2007 Screening for 8 disorders (CHT, PKU, CAH, GAL, CF, Public nationwide mandated
Hemoglobinopathies, Sickle cell disease, G6PDD)
Paraguay 2004 Screening for 3 disorders (CHT, PKU, CF) Public nationwide
Perú 2012 Screening for 5 disorders (CHT, PKU, GAL, CAH, CF) Public nationwide
Uruguay 1994 Screening for 28 disorders including CHT, PKU, CAH, CF, Public nationwide
Hemoglobinopathies, and additional 23 metabolic Among the most comprehensive public programs in
conditions including MSUD, other amino acid disorders, LATAM
fatty acid oxidation disorders, and organic acidurias
Venezuela 1999 Screening for 2 disorders (CHT, PKU) Public nationwide
NBS: Newborn screening; ENBS: expanded newborn screening; CHT: congenital hypothyroidism; PKU: phenylketonuria; MCADD: medium-chain
acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency; CF: cystic fibrosis; GAL: galactosemia; CAH: congenital adrenal hyperplasia; BTD: biotinidase deficiency;
MSUD: maple syrup urine disease; G6PDD: glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency.
The Mexican healthcare system is complex and fragmented, with multiple public healthcare providers
serving different fractions of the population according to their employment affiliation or lack thereof. A
child born in Mexico will receive medical care, including NBS, depending on the employment affiliation of
their parents. Petroleos Mexicanos (PEMEX) is the Mexican national oil company and it has a network of
hospitals and clinics across the country that is available to workers of the company and their families and
serves about 1.2% of the Mexican population. The PEMEX Genetics Department has since 2005
implemented the most comprehensive public metabolic ENBS program in Mexico with the screening of
69 conditions initially through MS/MS, and later in 2012 with the expansion to 76 inborn errors of
metabolism (IEM) disorders, SCID, and six lysosomal storage disorders (LSDs), namely Fabry, Gaucher,
Pompe, Krabbe, Hurler, and Niemann-Pick diseases . Between January 2005 and December 2019, PEMEX
[6]
screened 65,600 newborns born within their hospital system. Of those, 806 newborns were found to have a
positive screen test by ENBS and confirmed to have a genetic disorder. Of these, 779 were confirmed to
have an inborn error of metabolism, 25 were positive for a lysosomal storage disorder, and 2 were found to
have a congenital immunodeficiency . G6PDD was the most commonly identified condition (1 in 178
[7]
newborns), followed by transient neonatal tyrosinemia (TNT, 1 in 194 newborns). A positive screening