Page 745 - Read Online
P. 745
Vandiver et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2020;7:63 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2020.159 Page 9 of 14
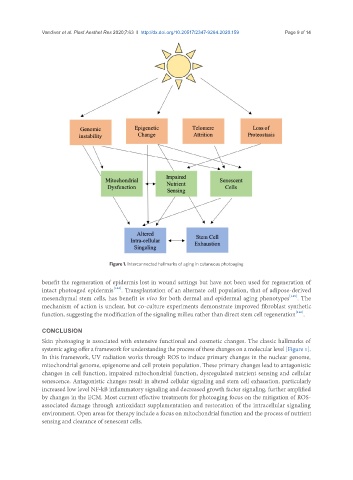
Figure 1. Interconnected hallmarks of aging in cutaneous photoaging
benefit the regeneration of epidermis lost in wound settings but have not been used for regeneration of
intact photoaged epidermis [144] . Transplantation of an alternate cell population, that of adipose-derived
mesenchymal stem cells, has benefit in vivo for both dermal and epidermal aging phenotypes [145] . The
mechanism of action is unclear, but co-culture experiments demonstrate improved fibroblast synthetic
function, suggesting the modification of the signaling milieu rather than direct stem cell regeneration [146] .
CONCLUSION
Skin photoaging is associated with extensive functional and cosmetic changes. The classic hallmarks of
systemic aging offer a framework for understanding the process of these changes on a molecular level [Figure 1].
In this framework, UV radiation works through ROS to induce primary changes in the nuclear genome,
mitochondrial genome, epigenome and cell protein population. These primary changes lead to antagonistic
changes in cell function, impaired mitochondrial function, dysregulated nutrient sensing and cellular
senescence. Antagonistic changes result in altered cellular signaling and stem cell exhaustion, particularly
increased low level NF-kB inflammatory signaling and decreased growth factor signaling, further amplified
by changes in the ECM. Most current effective treatments for photoaging focus on the mitigation of ROS-
associated damage through antioxidant supplementation and restoration of the intracellular signaling
environment. Open areas for therapy include a focus on mitochondrial function and the process of nutrient
sensing and clearance of senescent cells.