Page 423 - Read Online
P. 423
Singh et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2020;7:39 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2019.76 Page 5 of 13
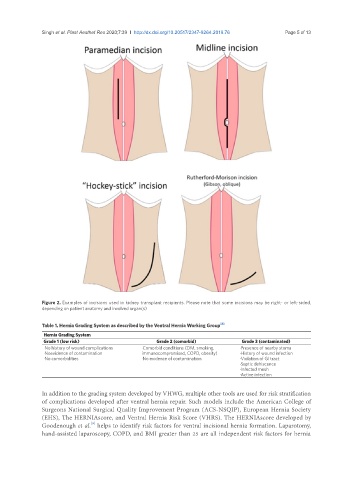
Figure 2. Examples of incisions used in kidney transplant recipients. Please note that some incisions may be right- or left-sided,
depending on patient anatomy and involved organ(s)
Table 1. Hernia Grading System as described by the Ventral Hernia Working Group [8]
Hernia Grading System
Grade 1 (low risk) Grade 2 (comorbid) Grade 3 (contaminated)
·No history of wound complications ·Comorbid conditions (DM, smoking, ·Presence of nearby stoma
·Noevidence of contamination immunocompromised, COPD, obesity) ·History of wound infection
·No comorbidities ·No evidence of contamination ·Violation of GI tract
·Septic dehiscence
·Infected mesh
·Active infection
In addition to the grading system developed by VHWG, multiple other tools are used for risk stratification
of complications developed after ventral hernia repair. Such models include the American College of
Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program (ACS-NSQIP), European Hernia Society
(EHS), The HERNIAscore, and Ventral Hernia Risk Score (VHRS). The HERNIAscore developed by
[9]
Goodenough et al. helps to identify risk factors for ventral incisional hernia formation. Laparotomy,
hand-assisted laparoscopy, COPD, and BMI greater than 25 are all independent risk factors for hernia