Page 395 - Read Online
P. 395
Paap et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2020;7:36 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2020.121 Page 5 of 11
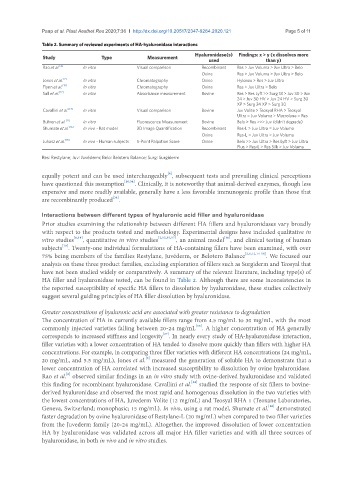
Table 2. Summary of reviewed experiments of HA-hyaluronidase interactions
Hyaluronidase(s) Findings: x > y (x dissolves more
Study Type Measurement used than y)
Rao et al. [6] In vitro Visual comparison Recombinant Res > Juv Voluma > Juv Ultra > Belo
Ovine Res > Juv Voluma > Juv Ultra > Belo
Jones et al. [2] In vitro Chromatography Ovine Hylenex > Res > Juv Ultra
Flynn et al. [15] In vitro Chromatography Ovine Res > Juv Ultra > Belo
Sall et al. [12] In vitro Absorbance measurement Bovine Res > Res Lyft >> Surg 18 > Juv 30 > Juv
24 > Juv 30 HV > Juv 24 HV > Surg 30
XP > Surg 24 XP > Surg 30
Cavallini et al. [14] In vitro Visual comparison Bovine Juv Volite > Teosyal RHA > Teosyal
Ultra = Juv Voluma > Macrolane = Res
Buhren et al. [17] In vitro Fluorescence Measurement Bovine Belo > Res >>> Juv (didn’t degrade)
Shumate et al. [16] In vivo - Rat model 3D Image Quantification Recombinant Res-L > Juv Ultra = Juv Voluma
Ovine Res-L = Juv Ultra > Juv Voluma
Juhasz et al. [18] In vivo - Human subjects 5-Point Palpation Score Ovine Belo >> Juv Ultra > Res Lyft > Juv Ultra
Plus > Res-L > Res Silk > Juv Voluma
Res: Restylane; Juv: Juvéderm; Belo: Belotero Balance; Surg: Surgiderm
[6]
equally potent and can be used interchangeably , subsequent tests and prevailing clinical perceptions
have questioned this assumption [16,34] . Clinically, it is noteworthy that animal-derived enzymes, though less
expensive and more readily available, generally have a less favorable immunogenic profile than those that
[34]
are recombinantly produced .
Interactions between different types of hyaluronic acid filler and hyaluronidase
Prior studies examining the relationship between different HA fillers and hyaluronidases vary broadly
with respect to the products tested and methodology. Experimental designs have included qualitative in
[16]
vitro studies [6,14] , quantitative in vitro studies [2,12,15,17] , an animal model , and clinical testing of human
[18]
subjects . Twenty-one individual formulations of HA-containing fillers have been examined, with over
75% being members of the families Restylane, Juvéderm, or Belotero Balance [2,6,12,14-18] . We focused our
analysis on these three product families, excluding exploration of fillers such as Surgiderm and Teosyal that
have not been studied widely or comparatively. A summary of the relevant literature, including type(s) of
HA filler and hyaluronidase tested, can be found in Table 2. Although there are some inconsistencies in
the reported susceptibility of specific HA fillers to dissolution by hyaluronidase, these studies collectively
suggest several guiding principles of HA filler dissolution by hyaluronidase.
Greater concentrations of hyaluronic acid are associated with greater resistance to degradation
The concentration of HA in currently available fillers range from 4.5 mg/mL to 30 mg/mL, with the most
[13]
commonly injected varieties falling between 20-24 mg/mL . A higher concentration of HA generally
[27]
corresponds to increased stiffness and longevity . In nearly every study of HA-hyaluronidase interaction,
filler varieties with a lower concentration of HA tended to dissolve more quickly than fillers with higher HA
concentrations. For example, in comparing three filler varieties with different HA concentrations (24 mg/mL,
[2]
20 mg/mL, and 5.5 mg/mL), Jones et al. measured the generation of soluble HA to demonstrate that a
lower concentration of HA correlated with increased susceptibility to dissolution by ovine hyaluronidase.
[6]
Rao et al. observed similar findings in an in vitro study with ovine-derived hyaluronidase and validated
[14]
this finding for recombinant hyaluronidase. Cavallini et al. studied the response of six fillers to bovine-
derived hyaluronidase and observed the most rapid and homogenous dissolution in the two varieties with
the lowest concentrations of HA, Juvederm Volite (12 mg/mL) and Teosyal RHA 1 (Teoxane Laboratories,
[16]
Geneva, Switzerland; monophasic; 15 mg/mL). In vivo, using a rat model, Shumate et al. demonstrated
faster degradation by ovine hyaluronidase of Restylane-L (20 mg/mL) when compared to two filler varieties
from the Juvederm family (20-24 mg/mL). Altogether, the improved dissolution of lower concentration
HA by hyaluronidase was validated across all major HA filler varieties and with all three sources of
hyaluronidase, in both in vivo and in vitro studies.